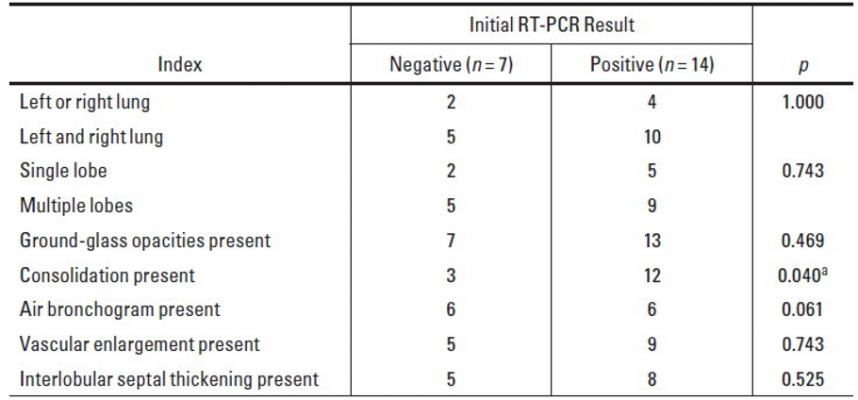
Comparison of CT features between groups with negative and positive initial RT-PCR results.
aThe difference was statistically significant in comparison of the two groups (p < 0.05).
June 18, 2020 — An open-access American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) article exploring the diagnostic value of chest computed tomography (CT) for coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia — especially for patients with negative initial results of reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing — found that the less pulmonary consolidation on chest CT, the greater the possibility of negative initial RT-PCR results.
From January 19 to February 20, 2020, lead investigator Dandan Chen of Guangzhou First People’s Hospital in China obtained the admission data of 21 patients (nine men, 12 women; age range, 26–90 years) with confirmed COVID-19 pneumonia from five nonspecialized infectious disease hospitals across Guangzhou.
After undergoing chest CT and swab RT-PCR tests within 3 days, patients were divided into two groups: seven patients with negative initial results (who were found to have positive results after a second RT-PCR test 2 days later) and 14 patients with initial positive results.
“Most of the COVID-19 lesions were located in multiple lobes (67%) in both lungs (72%) in our study,” Chen et al. wrote, adding that the CT findings observed most frequently were ground-glass opacities (95%) and consolidation (72%) with subpleural distribution (100%). “Otherwise,” they continued, “33% of patients had other lesions around the bronchovascular bundle.”
Additional chest CT findings identified by Chen and colleagues included air bronchogram (57%), vascular enlargement (67%), interlobular septal thickening (62%), and pleural effusions (19%).
Ultimately, compared with the positive initial RT-PCR results group, CT of the group with negative initial RT-PCR results was less likely to indicate pulmonary consolidation (p < 0.05).
Acknowledging that RT-PCR detection can be affected by laboratory reagents, test method, and subjective operability, Chen noted that, theoretically, the multicenter nature of this study—five hospitals in four districts of Guangzhou (13 cases in Huadu, four in Baiyun, three in Yuexiu, one in Nansha)—should have reduced interference by such factors.
“When patients with suspected COVID-19 pneumonia who have an epidemiologic history and typical CT features have negative initial RT-PCR results,” the authors of this AJR article concluded, “repeated RT-PCR tests and patient isolation should be considered.”
For more information: www.ajronline.com


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026 









