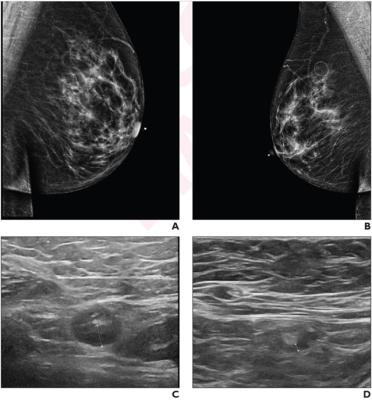
64-year-old woman who underwent screening mammography and breast ultrasound. A, right, and B, left, mediolateral oblique views obtained 2 days after booster dose of Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine administered in left upper extremity shows left axillary lymphadenopathy. No right axillary lymphadenopathy was visualized. C, left axillary ultrasound performed same day as mammogram shows enlarged left axillary lymph node (calipers) with thickened cortex, measuring 6 mm. D, left axillary ultrasound performed 102 days after booster dose shows normal lymph node (calipers) with cortical thickness of 2 mm, consistent with resolution of lymphadenopathy.
March 13, 2023 — According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), axillary lymphadenopathy after a COVID-19 vaccine booster dose has a mean time to resolution of 102 days, shorter than the time to resolution after the initial series.
“Findings support a follow-up interval of at least 12 weeks, as well as avoidance of delaying screening mammography, for suspected vaccine-related lymphadenopathy after booster doses,” concluded first author Eralda Mema, MD, of Weill Cornell Imaging at New York Presbyterian.
This AJR accepted manuscript retrospectively studied 54 patients (mean age, 57 years) at a single institution with unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy ipsilateral to a booster dose of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine visualized on ultrasound—whether an initial breast imaging examination or follow-up to prior screening or diagnostic breast imaging—performed between September 1, 2021 and December 31, 2022, and who underwent follow-up ultrasound examinations until resolution of lymphadenopathy. Electronic medical records were used to extract patient information.
Ultimately, axillary lymphadenopathy related to a booster dose of a COVID-19 vaccine resolved at a mean of 102 days after the booster dose and 84 days after the initial ultrasound examination showing the lymphadenopathy. Neither age, vaccine booster brand (Moderna vs. Pfizer), nor breast cancer history were significantly associated with time to resolution in univariable or multivariable analyses (all p>.05).
Noting exclusions due to incomplete or even unavailable vaccination history, patients were also excluded if follow-up imaging was pending, “which may have biased the sample toward inclusion of patients whose lymphadenopathy resolved rapidly,” the authors of this AJR accepted manuscript acknowledged.
For more information: www.arrs.org


 February 18, 2026
February 18, 2026