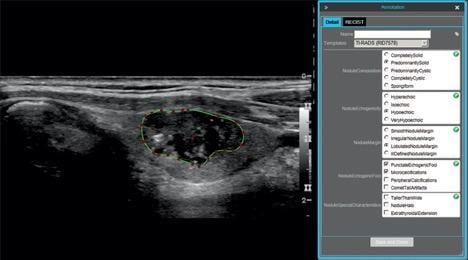
73-year-old man with papillary carcinoma of left lobe of thyroid. Screen shot shows example of thyroid nodule annotation (segmentation and TI-RADS annotation) performed on ultrasound image in longitudinal projection with electronic Physician Annotation Device software (Stanford Medicine Radiology). Radiologists performed nodule segmentation by selecting points (red) on nodule outline (green), while controlling smoothing of outline polygon by means of spline interpolation.
January 30, 2020 — According to an article published ahead-of-print in the April issue of the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), a Stanford University team has developed a quantitative framework able to sonographically differentiate between benign and malignant thyroid nodules at a level comparable to that of expert radiologists, which may prove useful for establishing a fully automated system of thyroid nodule triage.
Alfiia Galimzianova et al. retrospectively collected ultrasound images of 92 biopsy-confirmed nodules, which were annotated by two expert radiologists using the American College of Radiology’s Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS).
In the researchers’ framework, nodule features of echogenicity, texture, edge sharpness, and margin curvature properties were analyzed in a regularized logistic regression model to predict nodule malignancy. Authenticating their method with leave-one-out cross-validation, the Stanford team used ROC AUC, sensitivity, and specificity to compare the framework’s results with those obtained by six expert annotation-based classifiers.
The AUC of the proposed framework measured 0.828 (95% CI, 0.715–0.942) — "greater than or comparable,” Galimzianova noted, “to that of the expert classifiers”—whose AUC values ranged from 0.299 to 0.829 (p = 0.99).
Additionally, in a curative strategy at sensitivity of 1, use of the framework could have avoided biopsy in 20 of 46 benign nodules — statistically significantly higher than three expert classifiers. In a conservative strategy at specificity of 1, the framework could have helped to identify 10 of 46 malignancies — statistically significantly higher than five expert classifiers.
“Our results confirm the ultimate feasibility of computer-aided diagnostic systems for thyroid cancer risk estimation,” concluded Galimzianova. “Such systems could provide second-opinion malignancy risk estimation to clinicians and ultimately help decrease the number of unnecessary biopsies and surgical procedures.”
For more information: www.arrs.org


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026 









