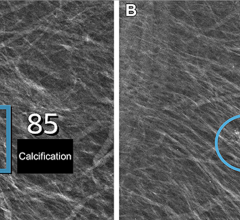
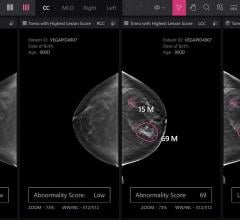
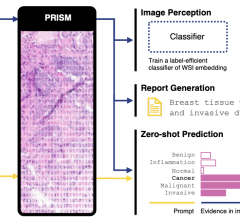
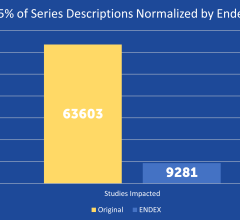
June 5, 2024 — Nano-X Imaging, an innovative medical imaging technology company, today announced that its deep-learning ...
Artificial Intelligence
This channel includes news and technology innovations for artificial intelligence (AI) software, also referred to as deep learning, cognitive computing and machine learning. AI technology is being integrated in radiology for imaging appropriate use criteria (AUC), clinical decision support, predictive analytics and to assist radiologists with improved workflow.
June 4, 2024 — Using artificial intelligence (AI), breast radiologists in Denmark have improved breast cancer screening ...
Did you know that approximately one-third of all the data in world is created by the healthcare industry and that ...
Despite decades of progress in breast imaging, one challenge continues to test even the most skilled radiologists ...
May 31, 2024 — To further the fight against global lung cancer, Qure.ai, a leader in healthcare artificial intelligence ...
May 30, 2024 — Paige, a global leader in end-to-end digital pathology solutions and artificial intelligence (AI) ...
May 29, 2024 — The Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) has launched the 2024 RSNA Lumbar Spine Degenerative ...
SPONSORED CONTENT — EnsightTM 2.0 is the newest version of Enlitic’s data standardization software framework. Ensight is ...
May 28, 2024 — iCAD, Inc., a global leader in clinically proven AI-powered cancer detection solutions, announced a ...
May 23, 2024 — NewVue.ai, born from the radiology technology pioneers behind peerVue and recognized as a trailblazer in ...
May 22, 2024 — Lunit, a provider of Artificial intelligence (AI)-powered solutions for cancer diagnostics and ...
Did you know that approximately one-third of all the data in world is created by the healthcare industry and that ...
May 22, 2024 — Lunit, a leading provider of AI-powered solutions for cancer diagnostics and therapeutics, recently ...
May 21, 2024 — According to a newly-published study of nearly 5,000 screening mammograms interpreted by an FDA-approved ...
May 16, 2024 — deepc, the globally recognized digital medicine pioneer and market leader behind the leading AI operating ...
Having the most efficient clinical workflows with enhanced diagnostic capabilities is a major goal for clinicians and ...
Having the most efficient clinical workflows with enhanced diagnostic capabilities is a major goal for clinicians and ...
May 15, 2024 — Heart disease is the leading cause of mortality in the U.S., accounting for one out of every five deaths ...
May 14, 2024 — Elekta announced the launch of its latest linear accelerator (linac), Evo*, a CT-Linac with new high ...
May 13, 2024 — Avenda Health, an AI healthcare company creating the future of personalized prostate cancer care, unveils ...
Radiology, once confined to dark rooms with X-ray films hanging from light boxes, has transformed at a rapid-fire pace ...
May 6, 2024 — ScreenPoint Medical’s Board of Directors has announced the appointment of Peter Kroese as the new Chief ...
May 2, 2024 — A new study from Mass General Brigham has found that large foundation models that incorporate a richer ...
May 2, 2024 — GE HealthCare has announced a new radiation therapy computed tomography (CT) solution with innovative ...

 June 05, 2024
June 05, 2024