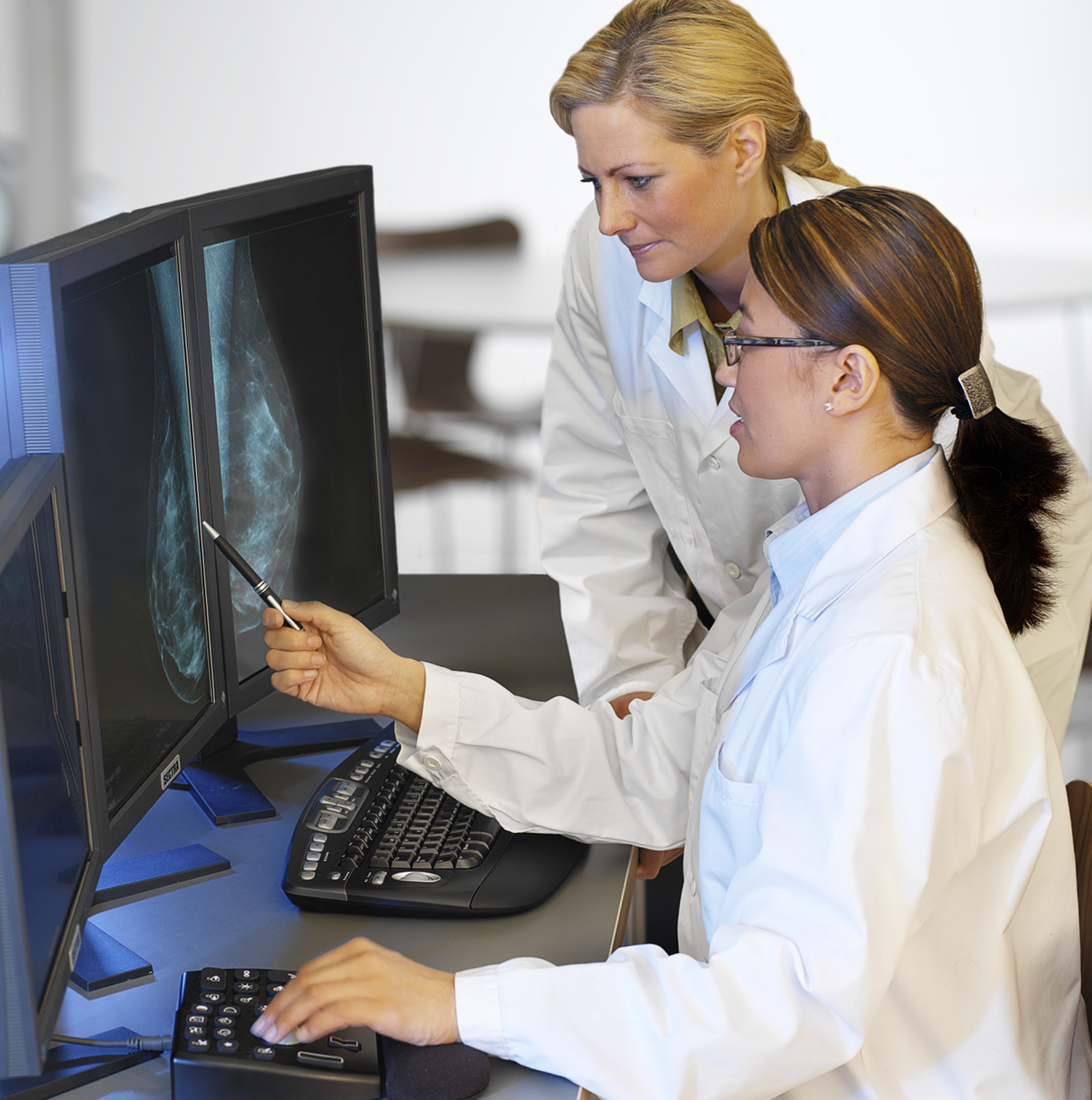
October 27, 2014 — Shear-wave elastography is set to become an important tool for detecting breast cancer, as it will reduce the number of breast biopsies performed and consequently ease the healthcare burden and decrease overall disease mortality, according to an analyst with research and consulting firm GlobalData.
The technique, which measures breast tissue elasticity, utilizes the knowledge that tumors and healthy tissue differ in this aspect, and has been shown to improve the specificity of breast ultrasound examinations without losing sensitivity.
Niharika Midha, MSc, GlobalData’s analyst covering medical devices, states that elastography has emerged as a promising technique for screening and diagnosing breast cancer and may be based either on the strain or the shear-wave method.
Midha explains: “While the strain method is capable of providing qualitative information, shear-wave elastography can generate quantitative data, as the elasticity of the tissue is measured in kilopascals. The quantitative method tracks the transverse shear waves spreading laterally from the breast tissue, calculating the speed of propagation.”
The analyst notes that while the technique is non-invasive, its clinical efficacy evaluation is limited by a lack of standardization in terms of compression of the tissue being examined, and in interpreting the elastography data.
Midha comments: “More prospective clinical studies are required to compare this technique’s diagnostic performance in different types of breast lesions. Furthermore, inter-instrument variability also needs to be assessed, as different manufacturers have incorporated this functionality into their premium ultrasound systems.”
The analyst adds that while mammography’s effectiveness has been the subject of debate among the medical community, a clear unmet need remains for the accurate and early detection of breast cancer, and for more robust screening and diagnostic techniques.
“Irrespective of its limitations, shear-wave elastography will play a vital role in the treatment of breast cancer, which sees 1.38 million new cases detected worldwide each year,” Midha concludes.
For more information: www.globaldata.com


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026