November 30, 2015 — Obese people who lose a substantial amount of weight can significantly slow knee cartilage degeneration, according to a new magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Obesity is a major risk factor for osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that affects more than a third of adults over the age of 60, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The knee joint is a common site of osteoarthritis, and in many people the condition progresses until total knee replacement becomes necessary. Aging baby boomers and a rise in obesity have contributed to an increased prevalence of knee osteoarthritis.
"Degenerative joint disease is a major cause of pain and disability in our population, and obesity is a significant risk factor," said the study's lead author, Alexandra Gersing, M.D., from the Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging at the University of California, San Francisco. "Once cartilage is lost in osteoarthritis, the disease cannot be reversed."
Gersing and colleagues recently investigated the association between different degrees of weight loss and the progression of knee cartilage degeneration in 506 overweight and obese patients from the Osteoarthritis Initiative, a nationwide research study focused on the prevention and treatment of knee osteoarthritis. The patients either had mild to moderate osteoarthritis or risk factors for the disease. They were divided into three groups: a control group who did not lose weight, a second group who lost a little weight, and a third group who lost more than 10 percent of their body weight. The researchers then used MRI to quantify knee osteoarthritis.
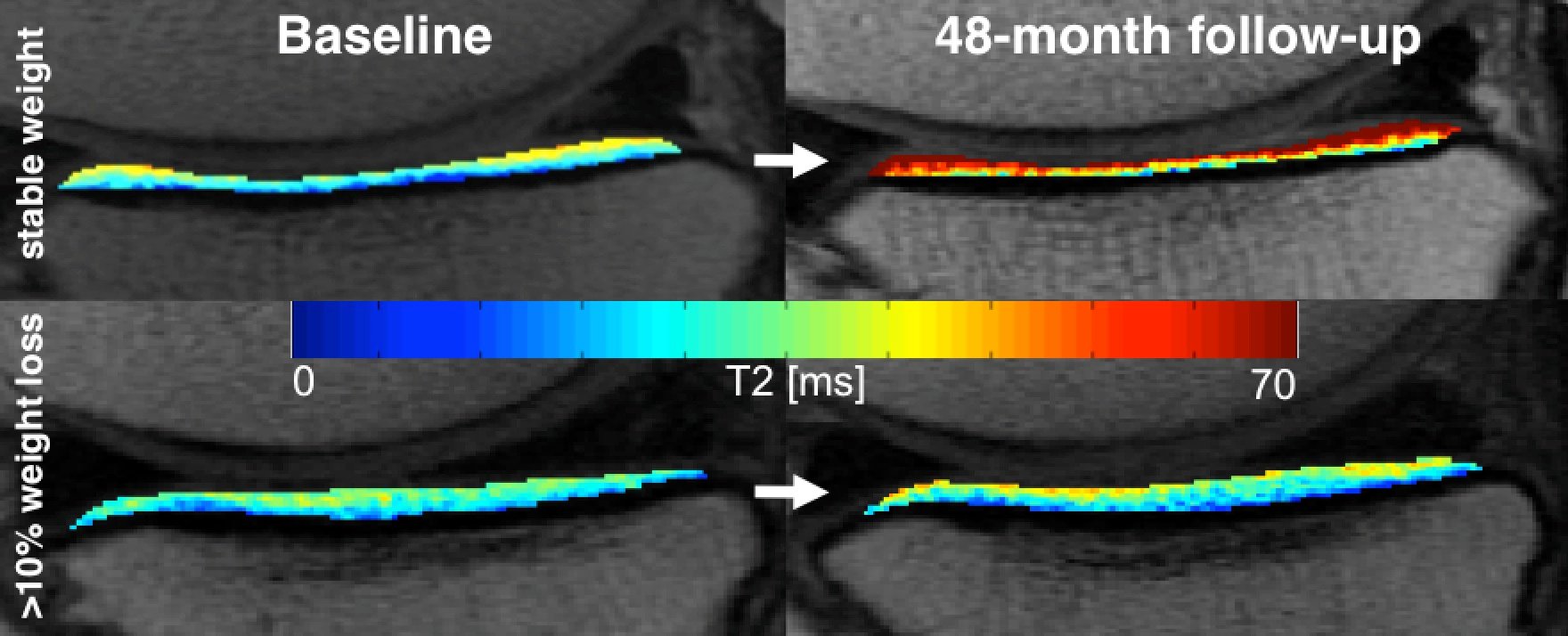
"Through T2 relaxation time measurements from MRI, we can see changes in cartilage quality at a very early stage, even before it breaks down," Gersing said.
When the researchers analyzed differences in the quality of cartilage among the three groups over a four-year time span, they found evidence that weight loss has a protective effect against cartilage degeneration and that a larger amount of weight loss is more beneficial.
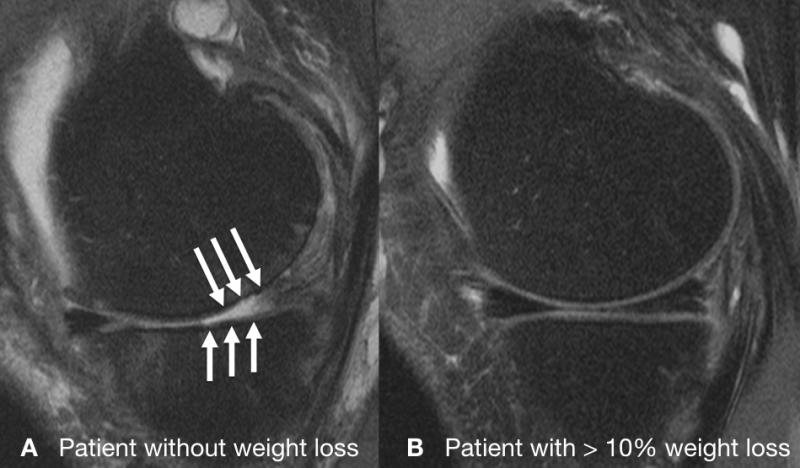
"Cartilage degenerated a lot slower in the group that lost more than 10 percent of their body weight, especially in the weight-bearing regions of the knee," Gersing said. "However, those with 5 to 10 percent weight loss had almost no difference in cartilage degeneration compared to those who didn't lose weight."
Substantial weight loss not only slows knee joint degeneration—it also reduces the risk of developing osteoarthritis, Gersing said. Along with moderate exercise, weight loss is one of the primary interventions against the disease.
"It's most helpful if these lifestyle interventions take place as early as possible," Gersing said.
In the future, the researchers are planning to study the role of diabetes, which is closely linked with obesity, in cartilage degeneration. They also plan to do an eight-year follow-up with the patient group and look at what effects weight gain may have on the knee joint.
Co-authors on the study are Martin Solka; Gabby B. Joseph, Ph.D.; Benedikt J. Schwaiger, M.D.; Ursula R. Heilmeier, M.D.; Georg Feuerriegel; John Mbapte Wamba, M.D.; Charles E. McCulloch, Ph.D.; Michael C. Nevitt, Ph.D.; and Thomas M. Link, M.D., Ph.D.
For more information: www.radiologyinfo.org


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026