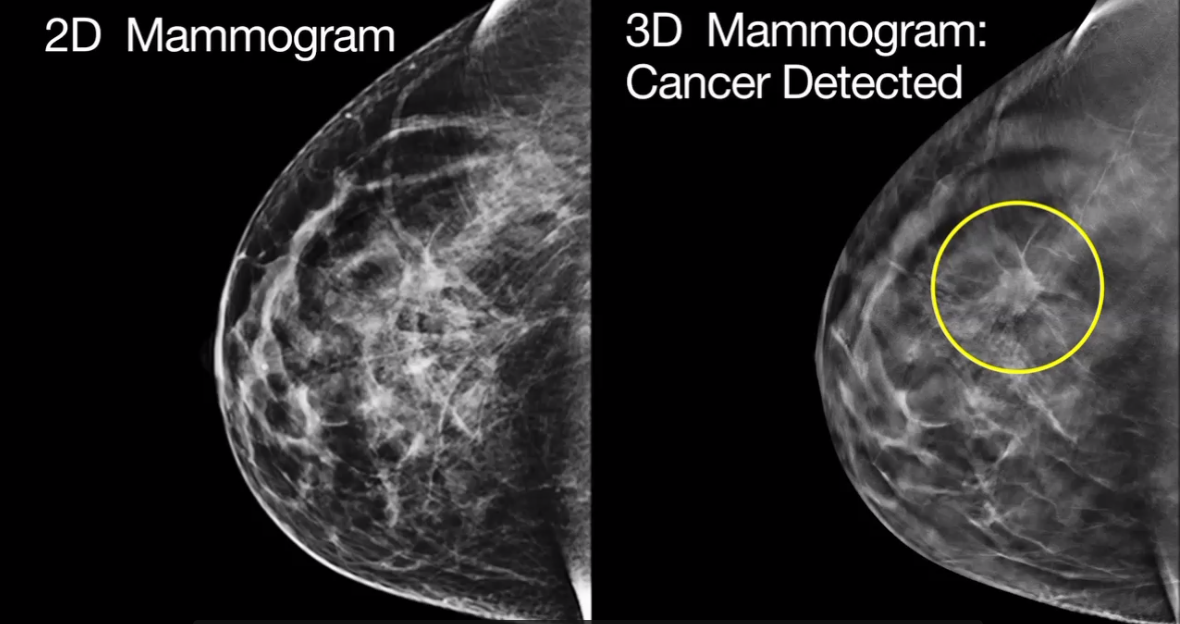
Digital
mammography is the gold standard for breast cancer screening, but may yield suspicious findings that turn out not to be cancer. These false-positive findings are associated with a higher recall rate.
Digital breast tomosynthesis has shown promise at reducing recall rates in all groups of patients, including younger
women and women with dense breast tissue. Tomosynthesis is similar to mammography in that it relies on ionizing radiation to generate
images of the breast. However, unlike conventional mammography, tomosynthesis allows for 3-D reconstruction of the breast tissue, which can then be viewed as sequential slices through the breast.
Because DBT technology is relatively new, it is typically used only as a supplemental screening tool, but since October 2011, every patient screened for breast cancer at Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania (HUP) in Philadelphia has been screened using DBT, according to Emily Conant, M.D., chief of breast imaging, HUP and lead author of the study.
"We have used DBT on all of our breast screening patients," said Conant. "Every patient has had it — we have not selected patients because of their risk or breast density or if they were willing to pay extra. We did not charge extra and were able to provide all of our women with this new technology."
For the study, Conant and colleagues compared imaging results from 15,633 women who underwent DBT at HUP beginning in 2011 to those of 10,753 patients imaged with digital mammography the prior year. Six radiologists trained in DBT interpretation reviewed the images.
The researchers found that, compared to digital mammography, the average recall rate using DBT decreased from 10.4 percent to 8.78 percent, and the cancer detection rate increased from 3.51 to 5.24 (per 1,000 patients). The overall positive predictive value — the proportion of positive screening mammograms from which cancer was diagnosed — increased from 4.1 percent to 6 percent with DBT.
"Our study showed that we reduced our callback rate and increased our cancer detection rate," said Conant. "The degree to which these rates were affected varied by radiologist. But importantly, the ratio of callback to cancer detection rate improved significantly for our radiologists."
Conant notes that tomosynthesis is an evolving platform, and researchers are already seeing a significant improvement in important screening outcomes.
"It's the most exciting improvement to mammography that I have seen in my career — even more important than the conversion from film-screen mammography to digital mammography," she said. "The coming years will be very exciting as we see further improvements in this technology."
Co-authors are Nandita Mitra, Ph.D., Anne Marie McCarthy, Ph.D., Despina Konto, Ph.D., Susan Roth, M.D., Susan Weinstein, M.D., Marie Synnestvedt, Ph.D., Mathew Thomas, B.S., and Fei Wan, Ph.D.