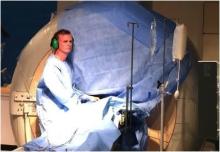
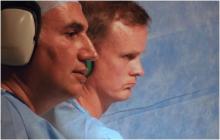
Imricor Medical Systems, Inc. announced the first three cardiac ablation procedures were completed in the first clinical study that is evaluating the feasibility of their magnetic resonance (MR)-enabled products to treat atrial flutter. Prof. Reza Razavi, head of the Division of Imaging Sciences and Biomedical Engineering, King's College London, is the principal investigator for the study and performed the procedures along with Mark O'Neill, professor of cardiac electrophysiology and consultant cardiologist, Guy's and St. Thomas' NHS Trust in the United Kingdom, The prospective pilot study will enroll up to 15 patients at this center.
© Copyright Wainscot Media. All Rights Reserved.
Subscribe Now