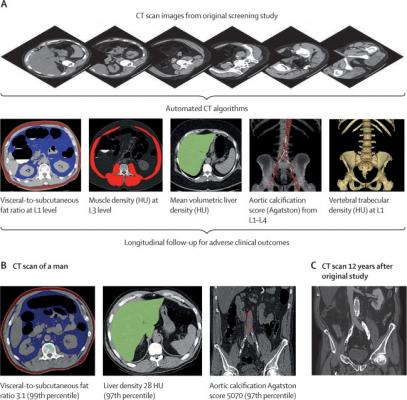
Figure 1: Depiction of the fully automated CT biomarkers tools used in this study. (A) Schematic depiction of the automated process for assessing fat, muscle, liver, aortic calcification, and bone from original abdominal CT scan data. (B) Case example in an asymptomatic 52-year-old man undergoing CT for colorectal cancer screening. At the time of CT screening, he had a body-mass index of 27·3 and Framingham risk score of 5% (low risk). However, several CT-based metabolic markers were indicative of underlying disease. Multivariate Cox model prediction based on these three CT-based results put the risk of cardiovascular event at 19% within 2 years, at 40% within 5 years, and at 67% within 10 years, and the risk of death at 4% within 2 years, 11% within 5 years, and 27% within 10 years. At longitudinal clinical follow-up, the patient suffered an acute myocardial infarction 3 years after this initial CT and died 12 years after CT at the age of 64 years. (C) Contrast-enhanced CT performed 7 months before death for minor trauma was interpreted as negative but does show significant progression of vascular calcification, visceral fat, and hepatic steatosis. HU=Hounsfield units.
March 6, 2020 — Researchers at the National Institutes of Health and the University of Wisconsin have demonstrated that using artificial intelligence to analyze computed tomography (CT) scans can produce more accurate risk assessment for major cardiovascular events than current, standard methods such as the Framingham risk score (FRS) and body-mass index (BMI).
More than 80 million body CT scans are performed every year in the U.S. alone, but valuable prognostic information on body composition is typically overlooked. In this study, for example, abdominal scans done for routine colorectal cancer screening revealed important information about heart-related risks — when AI was used to analyze the images.
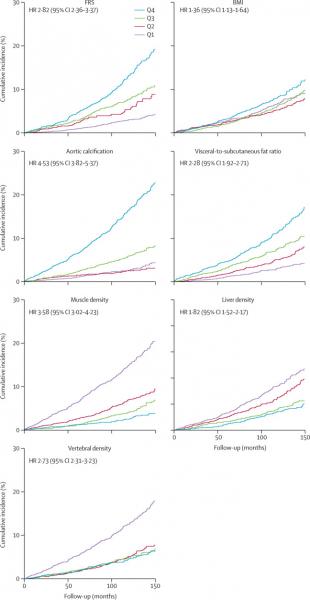
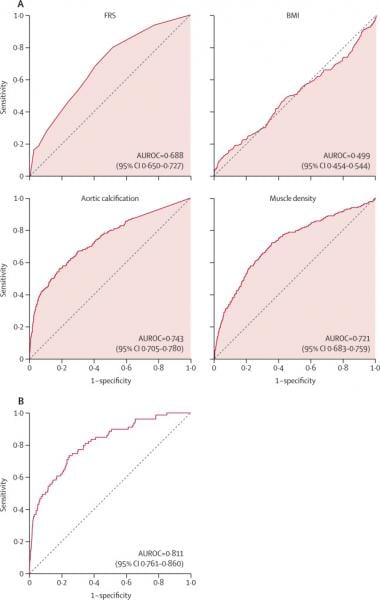
The study compared the ability of automated CT-based body composition biomarkers derived from image-processing algorithms to predict major cardiovascular events and overall survival against routinely used clinical parameters. The investigators found that the CT-based measures were more accurate than FRS and BMI in predicting downstream adverse events including death or myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident, or congestive heart failure. The results appeared in The Lancet Digital Health.
"We found that automated measures provided more accurate risk assessments than established clinical biomarkers," said Ronald M. Summers, M.D., Ph.D., of the NIH Clinical Center and senior author of the study. "This demonstrates the potential of an approach that uses AI to tap into the biometric data embedded in all such scans performed for a wide range of other indications and derive information that can help people better understand their overall health and risks of serious adverse events."
The study used five AI computer programs on abdominal CT scans to accurately measure liver volume and fatty change, visceral fat volume, skeletal muscle volume, spine bone mineral density, and artery narrowing. Researchers found that not only did the combination of automated CT-based biomarkers compare favorably with the FRS and BMI for predicting cardiovascular events and death before any symptoms were present but in fact, the CT measure of aortic calcification, that is buildup of calcium deposits in the aortic valve, alone significantly outperformed the FRS for major cardiovascular events and overall survival.
The researchers also observed that BMI was a poor predictor of cardiovascular events and overall survival, and all five automated CT-based measures clearly outperformed BMI for adverse event prediction.
"This opportunistic use of additional CT-based biomarkers provides objective value to what doctors are already doing," said Perry J. Pickhardt, M.D., of the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine & Public Health, lead and corresponding author of the study. "This automated process requires no additional time, effort, or radiation exposure to patients, yet these prognostic measures could one day impact patient health through presymptomatic detection of elevated cardiovascular or other health risks."
This research builds on prior efforts designing AI algorithms that Summers has undertaken in his lab in the NIH Clinical Center's Radiology and Imaging Sciences Department and his previous collaboration with Pickhardt to develop, train, test, and validate fully automated algorithms for measuring body composition using abdominal CT. The researchers plan to test the approach in other studies, including more racially diverse populations.
For more information: www.nih.gov


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026 









