As the imaging industry has looked for methods to achieve lower doses, especially in computed tomography (CT), many systems vendors have focused on utilizing software as one way to do it. GE Healthcare and Siemens are two of the companies offering dose reduction software technologies. Described below are their products and recent efforts.
• GE Healthcare has invested in technology for significantly lowering dose in CT procedures. Its ASiR (adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction) low-dose reconstruction technology is available on a variety of GE imaging platforms, including Discovery CT750 HD and LightSpeed VCT in the United States and BrightSpeed 16, Optima CT660 and others outside the United States. It was developed to help physicians significantly reduce dose while maintaining the high image quality and low contrast delectability they need for accurate diagnosis. In concert with the company’s SnapShot Pulse technology, ASiR also helps physicians dramatically reduce dose in cardiac imaging.
ASiR is used on more than 800 scanners worldwide. For more information, visit www.gehealthcare.com.
• In recent years, Siemens CT has contributed several innovations to reduce patient dose, starting with its first-generation CARE Dose4D, an automated tube current modulation, in 1994. Since then, other technologies to reduce dose have included the Adaptive Dose Shield, introduced on the Somatom Definition AS in 2007, and Flash Spiral imaging, on the Somatom Definition Flash in 2008. In 2009, it introduced IRIS (iterative reconstruction in image space), which was available on all Definition scanners.
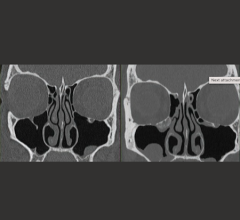
This year, Siemens will launch FAST CARE and a raw-data-based iterative reconstruction, SAFIRE (sinogram affirmed iterative reconstruction). With SAFIRE, raw data (or sinogram data) are utilized in the iterative image improvement process. (Results may vary; data are on file.)
The process is as follows:
• multiple iterative loops performed in the raw-data domain
• correction of geometrical imperfections
• reconstruct images from the “corrected” raw data
• multiple iterative loops performed in the image domain
• final images
For more information, visit www.usa.siemens.com/healthcare


 February 16, 2026
February 16, 2026