May 22, 2017 — Sigmascreening recently announced that a large independent Norwegian study further confirms Sigma’s hypothesis that pressure has a clear relation with the most optimal results in mammography. The study confirms the importance of pressure in accordance with Sigmascreening’s concept of the Sensitive Sigma Paddle , which applies pressure guidance during mammography. The combination of results of an earlier Dutch and this new Norwegian study shows an optimal pressure in the range of 10 kPa. This pressure clearly correlates very well with the proposed pressure by Sigmascreening, according to the company.
The data show that high breast volume and low compression pressure are associated with positive performance measures such as lower recall rate and higher specificity (true positive) of tumor detection. Procedures with too low pressures result in unnecessary recalls due to false positives. Flattening of the breast on the basis of pressure also prevents unnecessary discomfort and pain, which may contribute to a higher breast cancer screening compliance of women. The Sigma pressure technology aims to optimize these three elements.
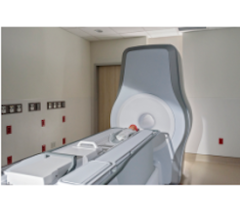
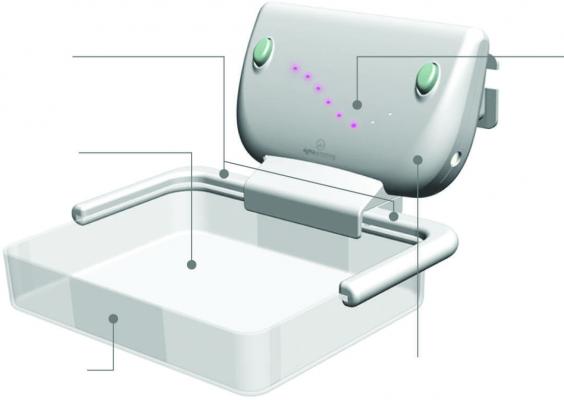
Sigmascreening’s Sensitive Sigma Paddle is the first pressure-based compression paddle providing real-time and reproducible information on mammographic pressure, which can considerably reduce frequently experienced pain for women during screening. It optimizes compression for every individual breast, taking into account breast size and tissue stiffness, which leads to an optimal mean contact pressure per woman, thereby optimizing both specificity (true negative) and sensitivity (true positive) for the most optimal screening result.
The data of the Norwegian retrospective study of 261,000 mammography exams, show that high breast volume and low compression pressure are associated with positive performance measures such as lower recall rate and higher specificity (true positive) of tumor detection. Especially the findings on the applied pressure are in line with earlier data generated in a Dutch study published in Breast Imaging by the research group of Prof. Nico Karssemeijer et al, in 54,137, showing that the performance of breast cancer screening also depends on mammographic compression. These studies confirm the philosophy behind Sigmascreening’s Sensitive Sigma Paddle for breast cancer screening devices.
The Norwegian researchers, led by Nataliia Moshina, M.D., a doctoral research fellow at the Cancer Registry of Norway in Oslo, categorized compression force and pressure to determine performance outcome measures such as recall rate, sensitivity, specificity and positive predictive value (PPV). "Based on our findings, low compression pressure and high breast volume are associated with favorable early performance measures, including lower recall rate, higher rate of screen-detected cancer and lower rate of interval breast cancer, compared with high compression pressure and low breast volume," the study authors wrote.
But apart from the screened and diagnosed women, radiographers and radiologists also benefit from pressure based compression. The real-time visualization of the applied pressure gives more insights into the compression practice, which leads to a faster, more pleasant and much more accurate procedure.
The Sensitive Sigma Paddle with CE marking is already being used in the United Kingdom, Norway, France, Germany, Sweden, The Netherlands, Belgium and Switzerland.
For more information: www.sigmascreening.com


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026