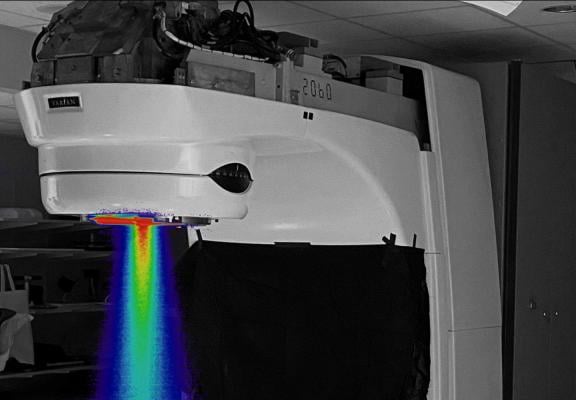
The exceptionally high dose rate of the FLASH Beam is 3,000 times higher than normal therapy treatment (300 Gray per second vs. 0.1 Gray per second, Gray being a standard unit measuring absorbed radiation). Instead of treatment over 20 seconds, an entire treatment is completed in 6 milliseconds, giving the therapy its nickname, "FLASH." Image courtesy of Brian Pogue, PhD
January 20, 2021 — A joint team of researchers from Radiation Oncology at Dartmouth's and Dartmouth-Hitchcock's Norris Cotton Cancer Center (NCCC), Dartmouth Engineering, and Dartmouth-Hitchcock's Department of Surgery have developed a method to convert a standard linear accelerator (LINAC), used for delivery of radiation therapy cancer treatment, to a FLASH ultra-high-dose rate radiation therapy beam. The work, titled "Electron FLASH Delivery at Treatment Room Isocenter for Efficient Reversible Conversion of a Clinical LINAC," is newly published online in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology & Physics.
The exceptionally high dose rate is 3,000 times higher than normal therapy treatment (300 Gray per second vs. 0.1 Gray per second, Gray being a standard unit measuring absorbed radiation). Instead of treatment over 20 seconds, an entire treatment is completed in 6 milliseconds, giving the therapy its nickname, "FLASH." "These high dose rates have been shown to protect normal tissues from excess damage while still having the same treatment effect on tumor tissues, and may be critically important for limiting radiation damage in patients receiving radiation therapy," said Brian Pogue, Ph.D., Co-Director of NCCC's Translational Engineering in Cancer Research Program and co-author on the project.
While the team awaits news of potential funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), early pilot funding from NCCC and Dartmouth's Thayer School of Engineering allowed for prototyping of the converted LINAC. Pre-clinical testing of the beam began in August and has already provided key data on its potential for different tumor plans. "This is the first such beam in New England and on the east coast, and we believe it is the first reversible FLASH beam on a clinically used LINAC where the beam can be used in the conventional geometry with patients on the treatment couch," said Pogue.
The FLASH beam is currently being used in preclinical studies on both experimental animal tumors as well as in clinical veterinary treatments, to study the normal tissue-sparing effects and how to maximize the value. The research group has expanded to involve physicians in clinical radiation oncology and dermatology, designing what they hope will be the first human safety trial with FLASH radiotherapy at Dartmouth-Hitchcock, treating patients advanced skin lesions that cannot be removed surgically.
For more information: https://www.dartmouth-hitchcock.org/


 February 04, 2026
February 04, 2026