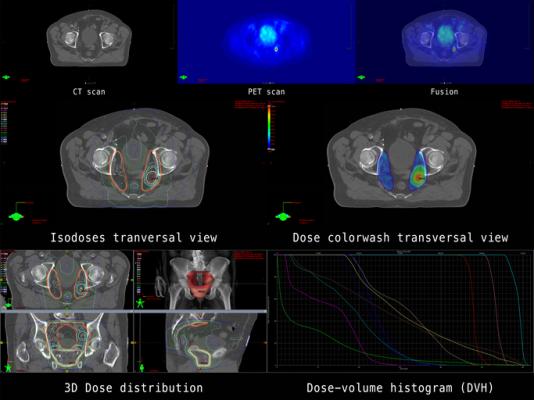
July 24, 2023 — A technique that uses imaging technology as a guide can make radiation therapy safer for patients with prostate cancer by helping clinicians accurately aim radiation beams at the prostate while avoiding nearby tissue in the bladder, urethra, and rectum. That is the finding of a thorough analysis of all published clinical trials of the technique, called magnetic resonance–guided daily adaptive stereotactic body radiotherapy (MRg-A-SBRT). The analysis is published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
By providing detailed images, MRg-A-SBRT can be used to adjust a patient’s radiation plan every day to account for anatomical changes and to monitor the position of the prostate in real time while the radiation beam is on to ensure that treatment is being directed accurately to the prostate. Although MRg-A-SBRT is becoming more popular and multiple clinical trials have tested it, it is unclear whether the technique, which requires more time and resources than standard procedures, has an impact on clinical outcomes and side effects compared with other ways of delivering radiation.
To investigate, Jonathan E. Leeman, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and his colleagues searched the medical literature for prospective studies that tested MRg-A-SBRT. The team combined data from 29 clinical trials that included a total of 2,547 patients to evaluate side effects that occurred following MRg-A-SBRT for prostate cancer compared with a more conventional method of treatment that is guided by computed tomography and is not adjusted on a daily basis in the way that MRg-A-SBRT is.
MRg-A-SBRT was associated with significantly fewer urinary and bowel side effects in the short term following radiation. Specifically, there was a 44% reduction in urinary side effects and a 60% reduction in bowel side effects.
“The study is the first to directly evaluate the benefits of MR-guided adaptive prostate radiation in comparison to another more standard and conventional form of radiation, and it provides support for use of this treatment in the management of prostate cancer,” said Dr. Leeman.
Dr. Leeman noted that the study also raises further questions regarding this type of treatment. For example, will the short-term benefits lead to long-term benefits, which are more impactful for patients? Longer follow-up will help answer this question because MRg-A-SBRT is a relatively new treatment. Also, which aspect of the technology is responsible for the improved outcomes seen in clinical trials? “It could potentially be the capability for imaging-based monitoring during the treatment or it could be related to the adaptive planning component. Further studies will be needed to disentangle this,” said Dr. Leeman.
An accompanying editorial discusses the analysis’ findings, weighs the potential benefits and shortcomings of adopting this treatment strategy for patients, and questions the value of broad adoption.
For more information: https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026 









