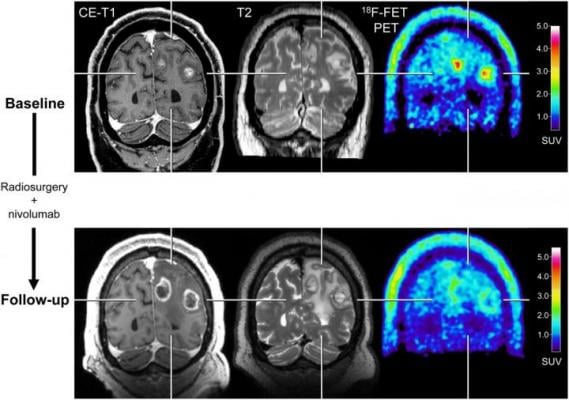
After radiosurgery concurrent with nivolumab in 59-year-old patient with melanoma BM (patient 1; Supplemental Tables 3 and 5), F-18 FET PET at follow-up 12 weeks after treatment initiation (bottom row) shows significant decrease of metabolic activity (TBRmean, ?28%) compared with baseline (top row), although MRI changes were consistent with progression according to iRANO criteria. Reduction of metabolic activity was associated with stable clinical course over 10 mo. CE = contrast-enhanced. Image created by N. Galldiks et al., Research Center Juelich, Juelich, Germany.
May 5, 2021 — For patients with brain metastases, amino acid positron emission tomography (PET) can provide valuable information about the effectiveness of state-of-the-art treatments. When treatment monitoring with contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is unclear, adding 18F-FET PET can help to accurately diagnose recurring brain metastases and reliably assess patient response. This research was published in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Newer treatment options for patients with brain metastases—such as immune checkpoint inhibitors and targeted therapies—are effective, but can cause a variety of side effects. As a result, imaging findings on contrast-enhanced MRI can be highly variable, and it can be difficult to tell whether a treatment is working.
"Essentially, these new treatments have requirements of brain imaging which cannot be met by conventional MRI," said Norbert Galldiks, M.D., professor of neurology, neurologist and neuro-oncologist at the University Hospital Cologne and Research Center in Juelich, Germany. "In our study, we tried to determine if adding 18F-FET PET could help to overcome some of these imaging challenges."
The retrospective study included melanoma and lung cancer patients with brain metastases who had been treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors or targeted therapy alone or in combination with radiotherapy. 18F-FET PET imaging was shown to be a useful method when conventional MRI was inconclusive. It could correctly diagnose brain metastasis relapses and identify patients who were responding to treatment and those who were not.
"In cases of ambiguous MRI findings, supplemental FET PET is helpful for treatment monitoring. It provides physicians with a longer time window for subsequent patient management and allows them to optimize the treatment strategy for each individual patient," noted Galldiks. "Since this approach is so accurate, it has the potential to influence clinical decision making. This may help to reduce the number of invasive procedures and limit overtreatment for a considerable number of seriously ill patients with brain metastases."
This study was made available online in September 2020 ahead of final publication in print in April 2021.
The authors of "Treatment Monitoring of Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy Using 18F-FET PET in Patients with Melanoma and Lung Cancer Brain Metastases: Initial Experiences," include Norbert Galldiks, Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany, Center of Integrated Oncology, Universities of Aachen, Bonn, Cologne, and Duesseldorf, Germany, and Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine (INM-3, -4), Research Center Juelich, Juelich, Germany; Diana S.Y. Abdulla, Matthias Scheffler and Jürgen Wolf, Center of Integrated Oncology, Universities of Aachen, Bonn, Cologne, and Duesseldorf, Germany, and Lung Cancer Group, Department I of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany; Fabian Wolpert and Michael Weller, Department of Neurology and Brain Tumor Center, University Hospital and University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland; Jan-Michael Werner and Gary Ceccon, Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany; Martin Hüllner, Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital and University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland; Gabriele Stoffels, Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine (INM-3, -4), Research Center Juelich, Juelich, Germany; Viola Schweinsberg, Max Schlaak, Nicole Kreuzberg and Cornelia Mauch, Center of Integrated Oncology, Universities of Aachen, Bonn, Cologne, and Duesseldorf, Germany, and Department of Dermatology, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany; Jennifer Landsberg, Center of Integrated Oncology, Universities of Aachen, Bonn, Cologne, and Duesseldorf, Germany, and Department of Dermatology, University Hospital Bonn, Bonn, Germany; Philipp Lohmann and Martin Kocher, Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine (INM-3, -4), Research Center Juelich, Juelich, Germany, and Department of Stereotaxy and Functional Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany; Christian Baues, Maike Trommer and Simone Marnitz, Center of Integrated Oncology, Universities of Aachen, Bonn, Cologne, and Duesseldorf, Germany, and Department of Radiation Oncology, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany; Eren Celik and Maximillian I. Ruge, Center of Integrated Oncology, Universities of Aachen, Bonn, Cologne, and Duesseldorf, Germany, and Department of Stereotaxy and Functional Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany; Gereon R. Fink, Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Cologne, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany, and Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine (INM-3, -4), Research Center Juelich, Juelich, Germany; Jörg-Christian Tonn, Department of Neurosurgery, University Hospital LMU Munich, Munich, Germany; and Karl-Josef Langen, Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine (INM-3, -4), Research Center Juelich, Juelich, Germany, and Department of Nuclear Medicine, RWTH University Hospital Aachen, Aachen, Germany.
For more information: www.snmmi.org


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026