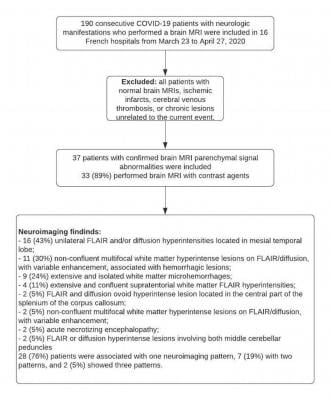
Figure 1. Flowchart of patient inclusion and exclusion.
October 20, 2020 — A new multi-institutional study published in the journal Radiology identifies patterns in abnormal brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings in patients with COVID-19.
Current data on central nervous system (CNS) involvement in COVID-19 is uncommon but growing, demonstrating a high frequency of neurological symptoms. However, the delineation of a large cohort of confirmed brain MRI abnormalities (excluding ischemic infarcts) related to COVID-19 has never been performed, and the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms remain unknown.
The purpose of this current study was to describe the neuroimaging findings other than stroke in patients with severe COVID-19 and report the clinical and biological profile of these patients.
The retrospective observational national multicenter study was initiated by the French Society of Neuroradiology (SFNR) in collaboration with neurologists, intensivists and infectious disease specialists. Consecutive patients with COVID-19 infection and neurologic manifestations who underwent brain MRI from March 23 to April 27, 2020, in 16 French centers, including 11 university hospitals and five general hospitals were included in the study.
Thirty men (81%) and 7 women (19%) met inclusion criteria, with a mean age of 61 years. The most common neurologic manifestations were alteration of consciousness (27/37, 73%), pathological wakefulness when the sedation was stopped (15/37, 41%), confusion (12/37, 32%) and agitation (7/37, 19%).
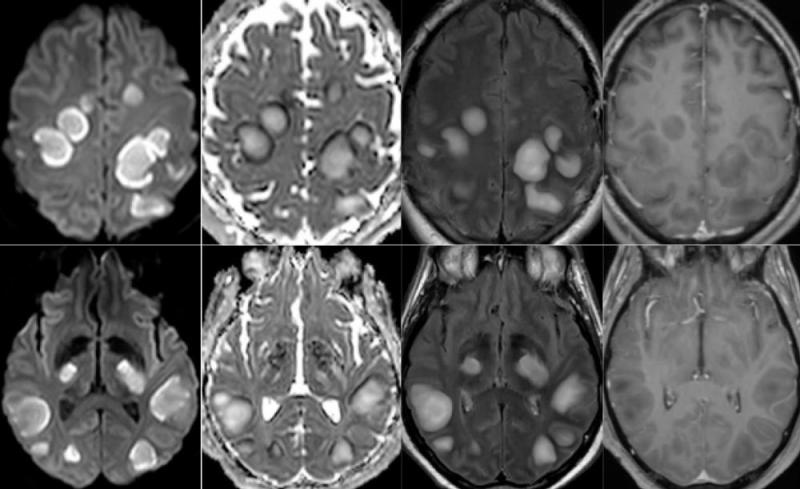
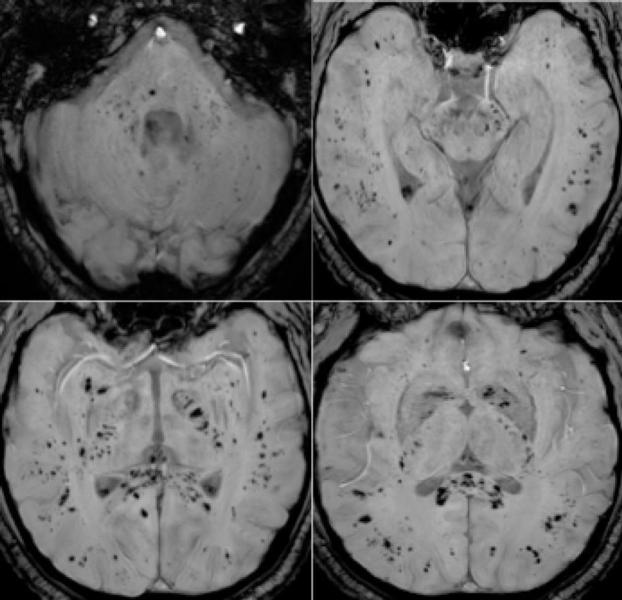
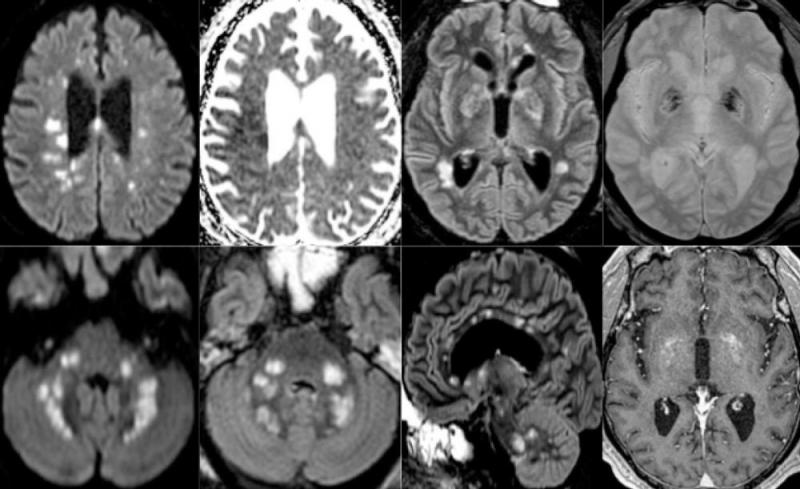
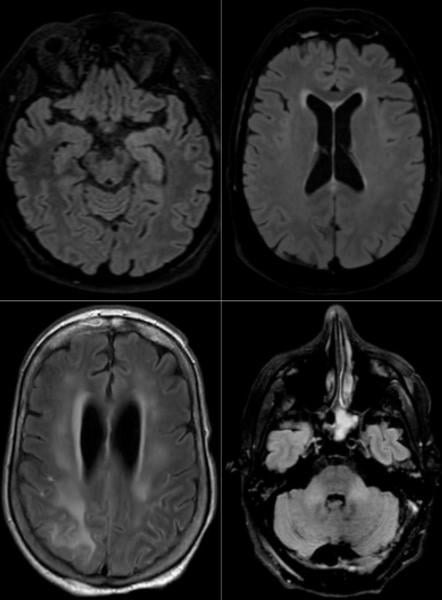
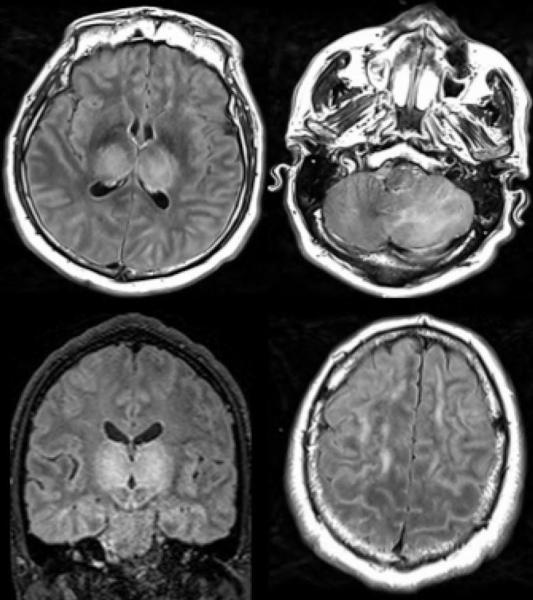
Among the 37 patients included, 28/37 (76%) were associated with one neuroimaging pattern, 7/37 (19%) with two patterns, and 2/37 (5%) showed three patterns. The most frequent MRI findings were: signal abnormalities located in the medial temporal lobe in 16/37 (43%) patients, non-confluent multifocal white matter hyperintense lesions on FLAIR and diffusion sequences, with variable enhancement, with associated hemorrhagic lesions in 11/37 patients (30%), and extensive and isolated white matter microhemorrhages in 9/37 patients (24%).
A majority of patients (20/37, 54%) had intracerebral hemorrhagic lesions and a more severe clinical presentation.
“Three main neuroradiological patterns could be distinguished, and the presence of hemorrhage was associated with worse clinical status. SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected in the cerebrospinal fluid in only one patient, and the underlying mechanisms of brain involvement remain unclear,” the authors wrote. “Imaging and neurological follow up has to be undertaken in order to evaluate the prognosis of these patients.”
For more information: www.rsna.org


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026 









