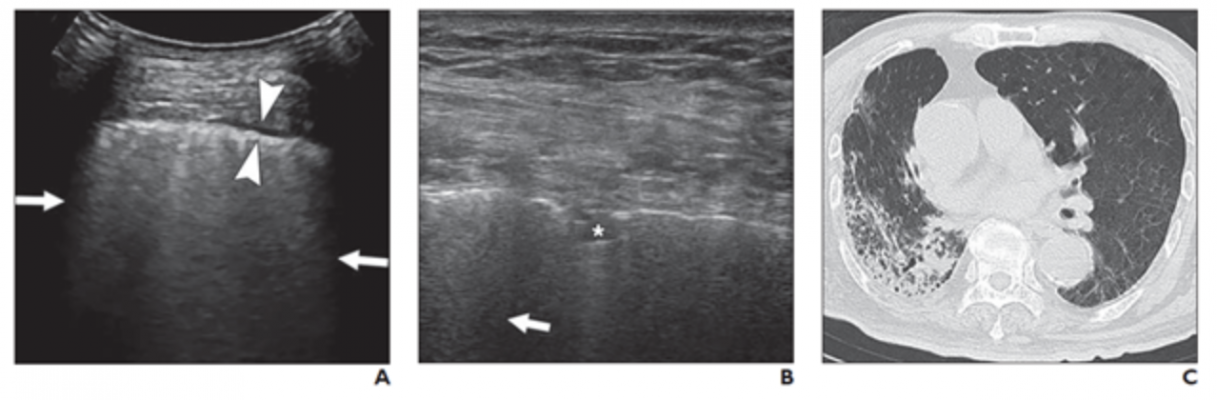
A and B, Lung ultrasound images obtained with convex (A) and linear (B) probes. Multiple confluent B-lines (arrows), patchy pulmonary consolidation (asterisk, B), and thickened pleural line (between arrowheads, A) are visualized. C, Chest CT image shows reticular and interlobular septal thickening and patchy, focal opacities associated with architectural distortion. This patient was classified in critical group and was assigned to severe group for statistical analysis.
July 23, 2020 — According to an open-access article published in ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), lung ultrasound (US) was highly sensitive for detecting abnormalities in patients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19), with B-lines, a thickened pleural line, and pulmonary consolidation the most commonly observed features.
“In addition,” concluded Yao Zhang of at China’s Beijing Ditan Hospital, “our results indicate that lung US findings can be used to reflect both the infection duration and disease severity.”
From March 3 to March 30, 2020, Zhang and colleagues performed lung US on consecutive patients with positive reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RTPCR) test results for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), using the Fisher exact test to compare the percentages of patients with each US finding between groups with different symptom durations and disease severity.
All 28 patients (14 men and 14 women; age range, 21–92 years) had positive findings on both lung US and chest computed tomography (CT). On US, B-lines were present in 100% of patients, and 19 (67.9%) patients had pulmonary consolidation. Thickened pleural lines were observed in 17 patients (60.7%), and only one patient (3.6%) showed a small amount of pleural effusion.
“A thickened pleural line was more frequently observed on US in patients with longer time intervals after the initial onset of symptoms,” Zhang et al. noted, adding that pulmonary consolidations — visualized as tissuelike hypoechoic regions, reflecting highly reduced air flow and increased quantity of inflammatory cellular exudate—were more common in severe and critical cases.
Acknowledging that portable radiography could be just as useful in evaluating consolidation, “a bedside portable, handheld US system or even a robot-assisted tele-US system (a unique technique for physicians to remotely scan patients) further minimizes the number of health care workers and medical devices exposed to COVID-19,” wrote Zhang and team.
The authors of this AJR article also proposed that severity scoring for lung US, similar to CT severity scores, should be developed to facilitate more accurate comparisons in future studies.
For more information: www.arrs.org


 March 09, 2026
March 09, 2026 









