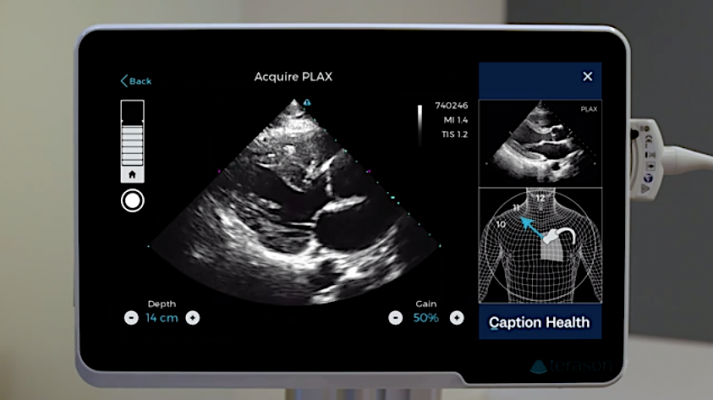
The Caption Guidance software uses artificial intelligence to guide users to get optimal cardiac ultrasound images in a point of care ultrasound (POCUS) setting.
February 13, 2020 — The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) cleared software to assist medical professionals in the acquisition of cardiac ultrasound, or echocardiography, images. The software, called Caption Guidance, is an accessory to compatible diagnostic ultrasound systems and uses artificial intelligence to help the user capture images of a patient’s heart that are of acceptable diagnostic quality.
The FDA granted marketing authorization of the Caption Guidance software to Caption Health Inc.
The Caption Guidance software is indicated for use in two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography (2-D TTE), for adult patients, specifically in the acquisition of standard views of the heart from different angles. These views are typically used in the diagnosis of various cardiac conditions.
“Echocardiograms are one of the most widely-used diagnostic tools in the diagnosis and treatment of heart disease,” said Robert Ochs, Ph.D., deputy director of the Office of In Vitro Diagnostics and Radiological Health in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “Today’s marketing authorization enables medical professionals who may not be experts in ultrasonography, such as a registered nurse in a family care clinic or others, to use this tool. This is especially important because it demonstrates the potential for artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies to increase access to safe and effective cardiac diagnostics that can be life-saving for patients.”
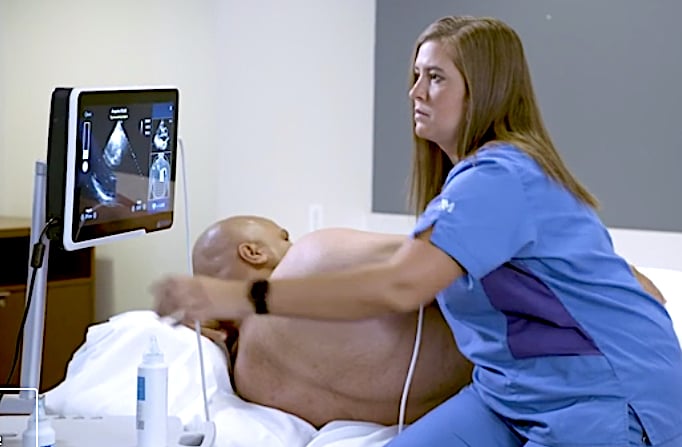
Caption Guidance will initially be deployed in acute point-of-care settings, including emergency and anesthesiology departments and critical care units, with plans to expand to additional departments. These settings serve a high volume of patients; emergency rooms alone are visited by one in five U.S. adults at least once per year.[1] In these environments, ultrasound can be used to triage, monitor, and assess patients who have chest pain, shortness of breath, cardiac arrest, and many other conditions, as well as for the detection of heart disease.
"Point-of-care ultrasound has been demonstrated to expedite time to diagnosis, reduce the need for more costly testing, and decrease complications from invasive procedures," said John Bailitz, M.D., system point of care ultrasound education director, Northwestern Medicine. "Caption Guidance can unlock these benefits by addressing one of the largest barriers to ultrasound adoption: the ability to acquire diagnostic quality images quickly."
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States, killing one out of every four people, or approximately 647,000 Americans each year. The term heart disease refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack. Other kinds of heart disease may involve the valves in the heart, or the heart may not pump well and cause heart failure.
The Caption Guidance software artificial intelligence shows a diagram of the patient and where to moved the ultrasound transducer to get standard echocardiography views and where to find the acustic windows. It is designed to help image diagnostic quality cardiac ultrasound images in a point of care ultrasound (POCUS) setting.
Cardiac diagnostic tests are necessary to identify heart conditions. Among them are electrocardiograms (EKG or ECG), Holter monitors and cardiac ultrasound examinations. The software authorized today is the first software authorized to guide users through cardiac ultrasound image acquisition.
The Caption Guidance software was developed using machine learning to train the software to differentiate between acceptable and unacceptable image quality. This knowledge formed the basis of an interactive AI user interface that provides prescriptive guidance to users on how to maneuver the ultrasound probe to acquire standard echocardiographic images and video clips of diagnostic quality. The AI interface provides real-time feedback on potential image quality, can auto-capture video clips, and automatically saves the best video clip acquired from a particular view. Importantly, the cardiologist still reviews the images for a final assessment of the images and videos for patient evaluation.
The Caption Guidance software currently can be used with a specific FDA-cleared diagnostic ultrasound system produced by Teratech Corp., with the potential to be used with other ultrasound imaging systems that have technical specifications consistent with the range of ultrasound systems used as part of the development and testing.
In its review of this device application, the FDA evaluated data from two independent studies. In one study, 50 trained sonographers scanned patients, with and without the assistance of the Caption Guidance software. The sonographers were able to capture comparable diagnostic quality images in both settings. The other study involved training eight registered nurses who are not experts in sonography to use the Caption Guidance software and asking them to capture standard echocardiography images, followed by five cardiologists assessing the quality of the images acquired. The results showed that the Caption Guidance software enabled the registered nurses to acquire echocardiography images and videos of diagnostic quality.
The FDA said is dedicated to ensuring medical device regulation keeps pace with technological advancements, such as this marketing authorization. In February 2020, the FDA is hosting a public workshop titled “Evolving Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Radiological Imaging” and seeks to discuss emerging applications of AI in radiological imaging, including AI devices intended to automate the diagnostic radiology workflow, as well as guided image acquisition. Discussions will also focus on best practices for the validation of AI-automated radiological imaging software and image acquisition devices, which is critical to assess safety and effectiveness.
The FDA reviewed the device through the De Novo premarket review pathway, a regulatory pathway for low- to moderate-risk devices of a new type. Along with this authorization, the FDA is establishing special controls for devices of this type, including requirements related to labeling and performance testing. When met, the special controls, along with general controls, provide reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness for devices of this type. This action creates a new regulatory classification, which means that subsequent devices of the same type with the same intended use may go through FDA’s 510(k) premarket process, whereby devices can obtain marketing authorization by demonstrating substantial equivalence to a predicate device.
Watch a short video showing the system in use.
Caption Guidance successfully met all four primary endpoints, meeting the pre-specified criteria for study success by acquiring images of sufficient quality for specific clinical assessments. Namely, the RNs successfully acquired limited echo exams for qualitative visual assessments of left ventricular size: 98.8%, 95% CI [96.7, 100]; left ventricular function: 98.8% [96.7, 100]; right ventricular size: 92.5% [88.1, 96.9]; and pericardial effusion: 98.8% [96.7, 100].
In 2018, the FDA granted Breakthrough Device designation to Caption Guidance. To qualify for such designation, a device must provide for more effective treatment or diagnosis of a life-threatening or irreversibly debilitating disease or condition, and meet additional criteria including being a breakthrough technology with no approved alternatives and offers significant advantages over existing alternatives.
Reference:


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026 









