April 1, 2016 — Augmenix Inc. announced the publication of the SpaceOAR System U.S. Clinical Trial results of the application technique and impact on prostate intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT).
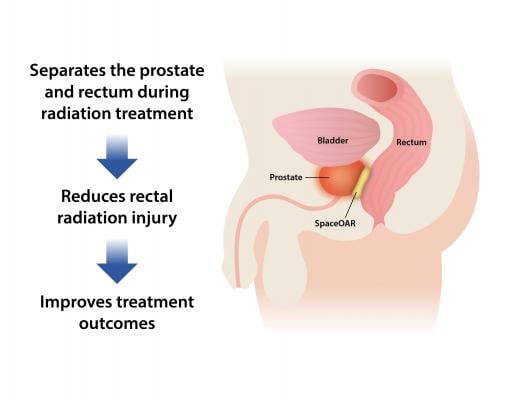
Designed to act as a temporary spacer, the absorbable hydrogel pushes the rectum away from the prostate and reduces rectal radiation injury in men undergoing prostate cancer radiotherapy.
Published in the March issue of Urology Practice, an official journal of the American Urological Association (AUA), the paper describes outcomes in a randomized, controlled Level 1 clinical trial evaluating IMRT in prostate cancer patients with (SpaceOAR) and without (control) the prostate-rectum spacing hydrogel.
“The simple concept of an absorbable spacer improving prostate radiotherapy outcomes makes so much sense,” said Lawrence I. Karsh, M.D., director of research and attending urologist, The Urology Center of Colorado and a study investigator. “I insist on the best care for my patients, and knowing this tool is now available increases my confidence in achieving excellent radiotherapy outcomes.”
Between 2010 and 2013, 222 patients with stage T1 or T2 prostate cancer were enrolled in 20 centers across the United States. Either local, monitored or general anesthesia was used in an outpatient procedure to implant the hydrogel spacer. Patient tolerance of the spacer implantation procedure was deemed excellent, with only 10 percent of the SpaceOAR patients experiencing mild transient effects (e.g. transient perineal discomfort). The hydrogel spacer increased the prostate-rectum space by an average of 11mm (1.6 to 12.6mm), resulting in a significantly reduced radiation dose to the rectum with no signs of altering the prostate dose or increasing dose elsewhere. Median rectal (v70) radiation dose was decreased by 78 percent in SpaceOAR patients relative to control (p<0.0001).
As anticipated, the reduced rectal radiation improved outcomes. Patients in the SpaceOAR group experienced 76 percent less acute rectal pain events, a 71 percent reduction in the incidence of late rectal toxicity, and significant reductions in late rectal toxicity severity. In addition, patients in the SpaceOAR group experienced lower rates of decline in bowel quality of life.
The hydrogel spacer was absorbed when evaluated 12 months after implantation and there were no implant infections, rectal wall complications or other issues related to the implant.
The device received clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April 2015. Augmenix will showcase the SpaceOAR System at the 111th AUA Annual Meeting, taking place May 6 - 10 in San Diego.
For more information: www.augmenix.com


 January 30, 2026
January 30, 2026