December 2, 2015 — Researchers in the Netherlands studying thousands of healthy adults have found a connection between very early stages of brain and heart disease. Results of their study were presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
"Heart and brain diseases are big problems in aging individuals and are expected to grow even more," said Hazel Zonneveld, M.D., M.Sc., from the Department of Epidemiology and Radiology at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam, Netherlands. "We know that myocardial infarction, heart failure and atrial fibrillation are associated with an increased risk of stroke and dementia. Our study investigates whether the heart-brain link is present at an earlier stage of disease."
Zonneveld and colleagues analyzed data from 2,432 participants in the Rotterdam Study (57.4 percent women, mean age 56.6 years), a prospective, population-based study designed to investigate chronic diseases in Rotterdam's aging population. Participants with overt heart disease, dementia and brain infarcts (strokes) were excluded from the analysis.
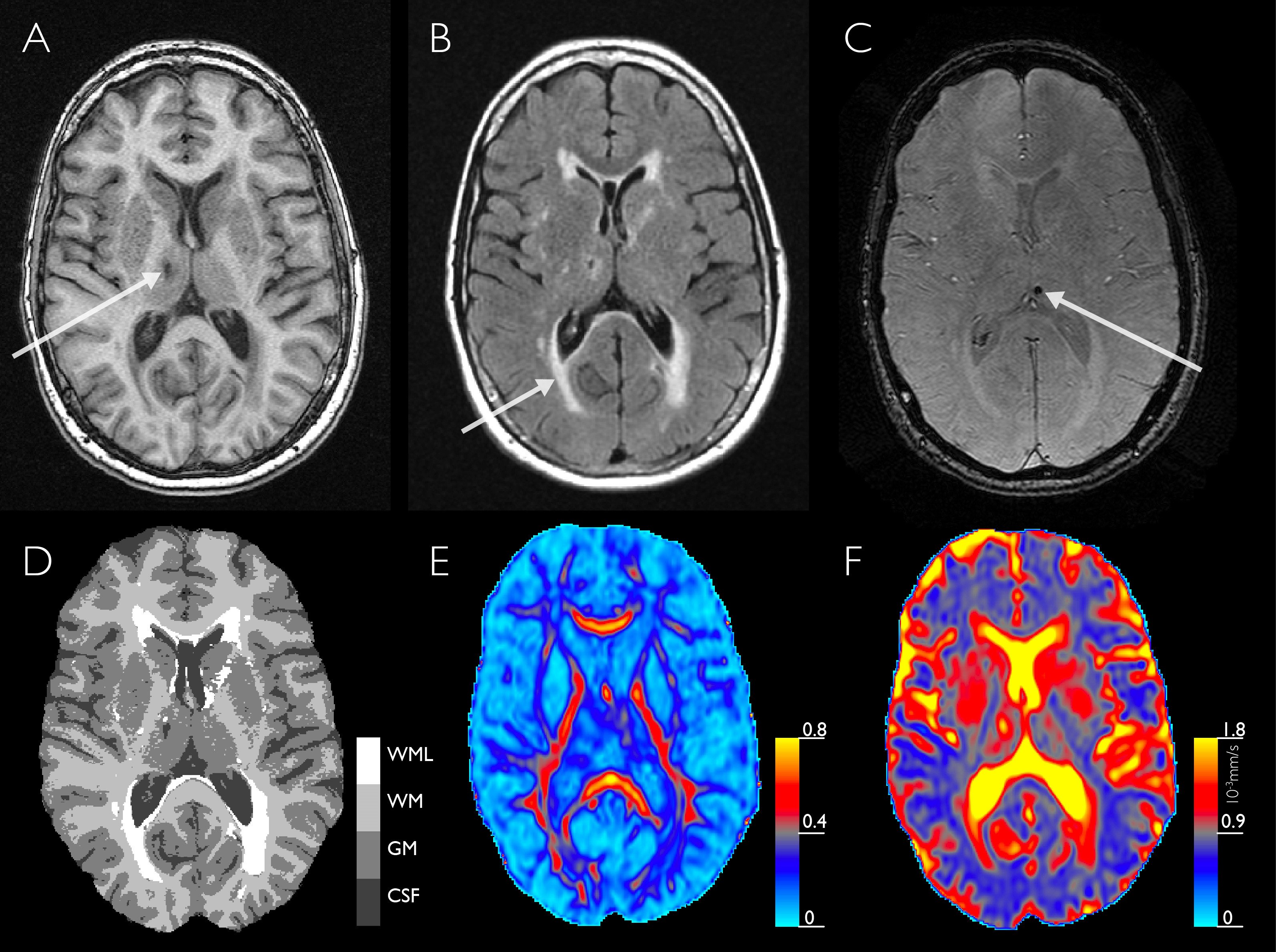
Participants in the study underwent brain MRI, which included the use of an advanced technique called diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), and blood testing to measure levels of N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), which is primarily used to help detect, diagnose and evaluate the severity of heart failure.
"NT-proBNP is released into the bloodstream in response to myocardial wall stress," Zonneveld said. "Studies have demonstrated that NT-proBNP provides information on cardiac dysfunction even in the absence of overt heart disease."
The researchers evaluated the brain MRI results for markers of early brain disease, including a loss of brain volume, microstructural changes and white matter lesions, which indicate areas of cells that have been damaged by injury or disease.
"Diffusion tensor imaging gives us information on the microstructural organization of the brain's white matter," Zonneveld said. "It is thought that microstructural brain changes precede brain changes, such as white matter lesions."
The results of DTI showed that participants with higher NT-proBNP levels had worse microstructural organization within the white matter. A statistical analysis revealed that higher NT-proBNP levels were also associated with smaller total brain volume and larger white matter lesion volume.
"The brain volume loss was predominantly in the gray matter," Zonneveld said.
According to Zonneveld, this study is the first to demonstrate an association between NT-proBNP and the microstructure of the brain.
"This implies that the heart and brain are intimately linked, even in presumably healthy individuals, and informs us importantly about development of disease as we age," she said.
Co-authors on the study are Wiro Niessen, Ph.D., Aad Van Der Lugt, M.D., Ph.D., Gabriel P. Krestin, M.D., Ph.D., Oscar H. Franco, M.D. Ph.D., M. Arfan Ikram, M.D, Ph.D., and Meike W. Vernooij, M.D, Ph.D.
For more information: RadiologyInfo.org


 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026