February 6, 2014 — Digital
mammography screening with photon-counting technique offers high diagnostic performance, according to a study published online in the journal
Radiology.
As mammography screening has shifted to digital technology, a range of
computed radiography (CR) and
direct radiography (DR) systems have emerged. The photon-counting technique is a DR approach that uses a detector to decrease scattered radiation and noise, enabling
dose reduction.
"In population-based mammography screening, dose reducing techniques that don't compromise outcome parameters are desirable," said Walter Heindel, M.D., department of clinical radiology at the University Hospital Muenster in Muenster, Germany.
For the
study, Heindel and colleagues analyzed data from the mammography screening program in North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state in Germany. They compared the screening performance of a DR photon-counting scan system with those of statewide operating screening units using different digital technologies. During the study period (2009 to 2010), 13,312
women were examined using the photon-counting system, and 993,822 women were screened with either CR or DR systems alone.
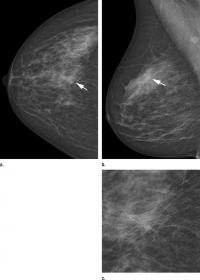
The DR photon-counting scan system had a cancer detection rate of 0.76 percent for subsequent screening, compared with 0.59 percent for the other screening units. The recall rate was 5.4 percent for the photon-counting method and 3.4 percent for the other methods.
"The higher cancer detection resulting from the use of the DR photon-counting scan system is due to high detection of both small, invasive cancers and ductal carcinoma in situ," Heindel said.
The photon-counting technique had almost twice the detection rate of other methods for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), an early, noninvasive form of disease. It had a higher DCIS detection rate than the statewide units and the conventional DR subgroup.
In addition, the mean average glandular radiation dose of the DR photon-counting scan system was significantly lower than the conventional DR systems with the individually used parameters of the automatic exposure control.
The photon-counting technique also offers lateral dose modulation during the image acquisition, which can help account for differences in breast density.
"One future research direction is the application of spectral imaging for quantification of breast glandular tissue, addressing the problem of breast density," Heindel said.
For more information: pubs.rsna.org/journal/radiology




 March 13, 2026
March 13, 2026