A new type of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) imaging system could enable surgeons and interventional radiologists to perform minimally invasive procedures under the guidance of 3-D images acquired during surgery with sub-millimeter spatial resolution. Medical physicists and engineers from the University Health Network in Toronto and Siemens Medical Solutions will present this technology at the 49th Annual Meeting of the American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM), taking place July 22-26, 2007.
Image-guided interventions have conventionally relied on image data acquired before the procedure on a diagnostic CT or magnetic resonance (MR) scanner. However, reliance on preoperative images does not allow visualization of changes imparted during a surgical procedure, such as seeing what remains of a tumor after it is removed.
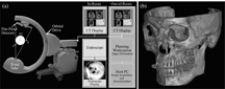
This imaging promises to overcome these conventional limitations by providing image updates during the procedure. One new technology showing particular promise is CBCT implemented on a surgical C-shaped arm.
Research at the University of Toronto, headed by Jeffrey Siewerdsen, in collaboration with clinical researchers at the University Health Network and at Siemens Medical Solutions (SMS), has yielded a 3-D imaging technology that could provide physicians with sub-millimeter spatial resolution and soft tissue visibility during surgery in near real-time. The technology involves the development of CBCT on a mobile C-arm to acquire a full-volume image in a single rotation around the patient.
While the image quality achieved with early cone-beam CT prototypes is not quite equivalent to that of a high-performance diagnostic CT scanner, image quality has been shown to be sufficient to guide surgeons and radiologists with respect to soft-tissue targets and critical structures.
Patients have been successfully treated with the prototype in a research setting, with trials underway in a broad spectrum of surgical and interventional procedures ranging from tumor ablation to orthopedic surgery and brachytherapy. High-quality intraoperative imaging provided by C-arm CBCT is expected to dramatically improve surgical performance and expand the application of minimally invasive interventions to cases that would be otherwise untreatable.


 January 30, 2026
January 30, 2026