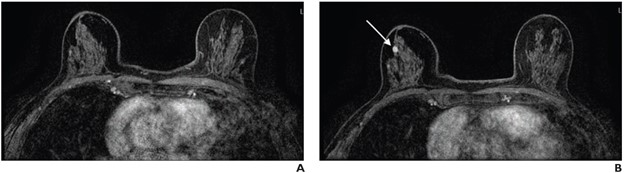
70-year-old-woman with extremely dense breasts. A. Axial subtracted contrast-enhanced fat-suppressed T1-weighted image from baseline AB-MR examination is negative (BI-RADS category 1). B. Axial subtracted contrast-enhanced fat-suppressed T1-weighted image from subsequent-round AB-MR examination performed 2 years later shows new 5-mm enhancing mass in upper outer right breast (arrow), which was not seen on mammogram performed 5 months prior. Examination was assessed as BI-RADS category 5. Ultrasound-guided core biopsy yielded invasive ductal carcinoma (ER+/PR+/HER2-).
June 6, 2024 — Subsequent rounds of abbreviated breast MRI (AB-MR) screening in patients with dense breasts had lower abnormal interpretation rate (AIR) compared to baseline examinations, while maintaining high cancer detection rate (CDR), according to the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR).
Pointing out that all cancers detected by subsequent-round examinations were early-stage node-negative cancers, “further investigations are warranted to optimize the screening interval,” noted first author Christine E. Edmonds, MD, from the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania. “The findings support sequential AB-MR for supplemental screening in individuals with dense breasts.”
Edmonds et al.’s AJR accepted manuscript included patients with dense breasts, at otherwise average breast-cancer risk, who underwent AB-MR for supplemental screening between December 20, 2016 and May 10, 2023. After extracting clinical interpretations and results of recommended biopsies for AB-MR examinations from the EMR, the researchers compared baseline and subsequent-round AB-MR examinations.
Ultimately, in women with dense breasts, subsequent-round AB-MR for supplemental screening achieved lower AIR versus baseline rounds (7.8% vs. 17.4%, p <.001), while maintaining high CDR (12.1 vs. 18.9 per 1000, p =.37). All cancers diagnosed by subsequent round AB-MR were stage 0 or 1; had size of 0.3-1.2 cm; and exhibited node-negative status.
For more information: www.arrs.org


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026