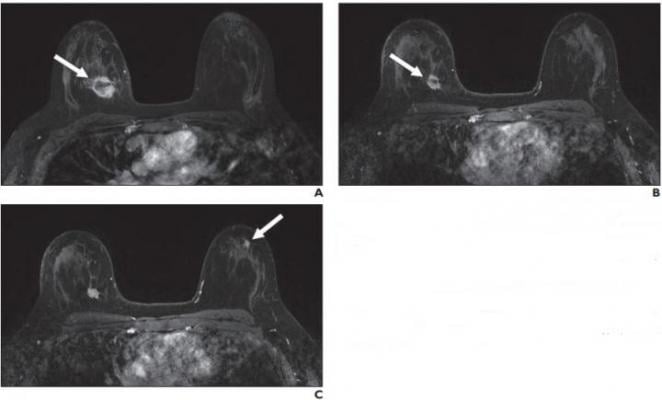
A, Contrast-enhanced axial T1-weighted fat-saturated image from baseline MRI before initiation of neoadjuvant therapy shows irregular mass (arrow) in upper inner right breast corresponding to biopsy-proven carcinoma. B, Contrast-enhanced axial T1-weighted fat-saturated image from follow-up MRI performed 3 months after initiation of neoadjuvant therapy shows decrease in size of right breast cancer (arrow). C, Contrast-enhanced axial T1-weighted fat-saturated image 3 months after initiation of neoadjuvant therapy shows new mass (arrow) in upper outer left breast that was assessed as BI-RADS 4. Pathologic examination from MRI-guided core biopsy of new suspicious mass revealed benign usual ductal hyperplasia. No atypia or malignancy was identified. Image courtesy of American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS), American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR)
January 15, 2021 — According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), new suspicious findings occurred in 5.5% of breast MRI examinations performed to monitor response to neoadjuvant therapy; none of these new lesions were malignant.
"Our findings suggest that new lesions that arise in the setting of neoadjuvant therapy are highly unlikely to represent a new site of malignancy, particularly if the index malignancy shows treatment response," wrote Donna A. Eckstein and colleagues in the department of radiology and biomedical imaging at the University of California, San Francisco.
Based on a presentation at the ARRS 2019 Annual Meeting, Honolulu, HI, the researchers' retrospective review pinpointed all breast MRI examinations performed to assess response to neoadjuvant therapy between 2010 and 2018. Cases with new suspicious lesions assessed as BI-RADS 4 or 5 and found after the initiation of neoadjuvant treatment were included. Meanwhile, exclusion criteria were cases with no pretreatment MRI, cases in which the suspicious lesion was present on the baseline MRI but remained suspicious, and cases with insufficient follow-up. Pathologic examination determined malignant outcomes, whereas benignity was established by pathologic examination, follow-up imaging, or both.
A total of 419 breast MRI examinations in 297 women (mean patient age, 45 years; range, 32-65 years) were performed to assess response to neoadjuvant treatment. After exclusions, 23 MRI examinations (5.5%) with new suspicious findings distinct from the site of known malignancy comprised the final study cohort. Of these 23 lesions, 13 new suspicious findings (56.5%) were contralateral to the known malignancy, nine (39.1%) were ipsilateral, and one (4.3%) involved the bilateral breasts. Lesion types included mass (16, 69.6%), nonmass enhancement (5, 21.7%), and focus (2, 8.7%).
Noting that, currently, there are no guidelines for the management of new suspicious imaging findings identified on MRI during the course of neoadjuvant systemic breast cancer treatment, "results in this small cohort suggest that these new findings are highly likely to be benign, particularly in the setting of response to therapy, which may potentially obviate biopsies in these patients in the future," wrote Eckstein et al.
"However," the authors of this AJR article concluded, "larger studies across different facilities are needed to confirm whether biopsy may be safely averted in this scenario."
For more information: www.arrs.org


 March 06, 2026
March 06, 2026