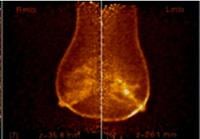
August 4, 2011 – Published last week in The American Journal of Roentgenology, researchers from Swedish Cancer Institute and the University of Washington used positron emission mammography (PEM) to find a correlation between fludeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake values and the prognostic factors that predict breast cancer survival. The highest FDG levels were in the most aggressive cancer type – triple negative cancers. Women with triple negative breast cancer have a higher mortality because there is no tailored therapy available to them. PEM may now benefit this patient population as it may help identify when a chemotherapeutic regimen is not working. PEM also has the potential to play a role in initial staging of breast cancer in patients at high risk for multifocal or multicentric disease who desire breast conservation therapy as an alternative to breast MRI.
PEM is the breast application of the Naviscan high-resolution PET scanner showing the location as well as the metabolic phase of a lesion. It is the only U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-cleared 3-D molecular breast imaging (MBI) device on the market. The metabolic view assists physicians in making optimal care decisions by providing an ability to distinguish between benign and malignant lesions, what researchers term "specificity."
Histologic grade, tumor size and expression of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and HER2/neu receptor are considered important prognostic variables in the clinical management of breast cancer. According to the publication authors, this is the first study to evaluate the correlation between prognostic indicators and FDG uptake values on PEM.
"PEM shows a significant positive correlation between FDG uptake and various prognostic factors since the advent of hormonal therapy such as hormone receptor status and histologic grade," stated Carolyn Wang, M.D., the lead author of the paper. "Lesion to background (LTB) may be a reflection of associated high-risk markers to be determined, and developing a sensitive imaging strategy for small tumors to complement immunohistochemical markers ER, PR, and HER2 may provide additional prognostic information at the molecular level. Further prospective studies will be needed to assess whether PEM FDG uptake is validated as an independent marker. This may affect treatment options and may be a marker to evaluate response to specific therapy."
PEM images from 98 newly diagnosed breast cancer patients with 100 lesions were reviewed by two physicians blinded to pathology results. Tumor FDG uptake and lesion to background (LTB) ratio levels were compared to ER, PR and HER2 receptor status. Results showed that high LTB ratio correlated with receptor status for ER-neg and PR-neg and that triple negative tumors had a higher LTB ratio. Breast tumors with higher histologic grade also had significantly higher FDG uptake than those with lower grade.
For more information: www.naviscan.com

 February 06, 2026
February 06, 2026 









