June 25, 2020 — The Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) and the RSNA COVID-19 AI Task Force today announced the launch of the RSNA International COVID-19 Open Radiology Database (RICORD). RICORD is envisioned as the largest open database of anonymized COVID-19 medical images in the world. More than 200 institutions around the world have expressed their interest in participating.
The database will include supporting clinical information and expert annotations. It will be freely available to the global research and education communities.
“The strong positive reaction speaks to the determination of the global radiology community to contribute its resources and expertise to addressing the pandemic,” said RSNA COVID-19 AI Task Force chair Matthew P. Lungren, M.D., M.P.H., assistant professor of radiology at Stanford University and associate director of the Stanford Center for Artificial Intelligence in Medicine and Imaging. “This effort is the result of countless hours by volunteer task force members and a broad community of radiologist annotators led by our close partners at the Society of Thoracic Radiology.”
Shortly after the first news of the pandemic, scientists isolated the virus and quickly sequenced the genome. The sequenced genome was immediately made available to the entire worldwide research community and became the inspiration for RICORD.
“This unprecedented spirit of collaboration accelerated clinical testing, therapeutic drug discovery, epidemiologic tracking and vaccine development,” Lungren said. “All of these advancements were completed in weeks to months, rather than the typical pace of months to years, and were catalyzed by this act of open-source scientific collaboration. This is perhaps one of the most dramatic examples of an open source research effort saving countless lives.”
RICORD aims to save lives via an open imaging database that can be used by the global research and education communities to gain new insights, apply new tools such as artificial intelligence and deep learning, and accelerate clinical recognition of this novel disease.
Radiologists and imaging departments in many countries have already found themselves on the front lines of this pandemic, particularly when other testing methods have fallen short or when clinicians seek imaging cues to guide therapy.
The RSNA COVID-19 AI Task Force hopes that RICORD will serve as a definitive source for COVID-19 imaging data by combining the contributions and experiences from radiologists around the world who have encountered the disease and gained invaluable clinical imaging experience that may also, if shared with others, save lives.
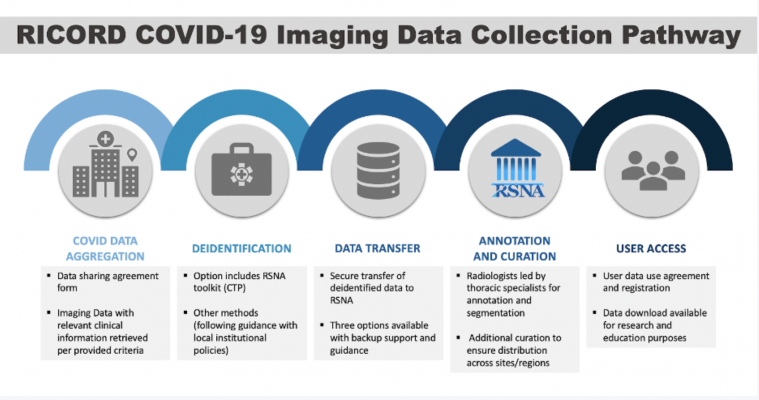
RSNA has also developed data sharing agreements and tools to organize, de-identify and transfer data. The RICORD data collection pathway enables radiology organizations to contribute data to RICORD safely and conveniently. It provides sites with guidance for data sharing and serves to standardize exam parameters, disease annotation terminology and clinical variables across these global efforts. In addition, it connects to sustainable storage infrastructure via the U.S. National Institutes of Health.
Substantial datasets have already been contributed to RICORD and are being used for education and research projects, including one that will develop a detailed annotation schema for COVID-19 imaging on CT.
RICORD v1.0 is the first annotated core dataset consisting of a subset of chest radiography and CT examinations in DICOM format with expert radiologist annotation labels. Over time, as data are ingested, curated and annotated, the RSNA COVID-19 AI Task Force will continue to update and expand both the volume and variety of data available in RICORD, including adding clinical variables and expanding to other imaging modalities.
“More than ever, this pandemic is showing us that we can rally together toward a common purpose,” Lungren said. “Rather than siloing data and pursuing fractured efforts, we can instead choose to collaborate through efforts like RICORD to accelerate an end to this pandemic as a united global imaging community.”
Sites interested in learning more or contributing data should visit the RICORD resources page.
For more information: RSNA.org/COVID-19

 May 17, 2024
May 17, 2024