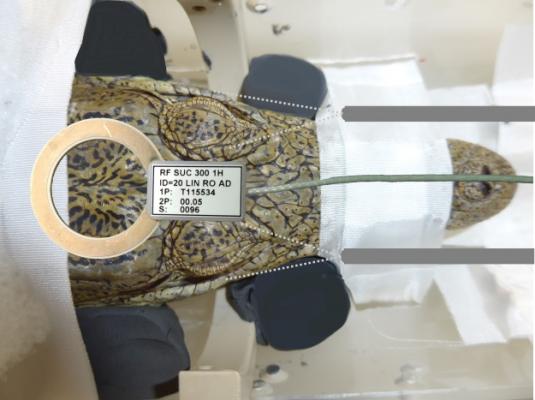
A research team from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) used functional MRI to assess the brain patterns of a Nile crocodile and determine what happens when the animal hears complex sounds. Image courtesy of Felix Ströckens, M.D./Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences
May 8, 2018 — In a first, an international research team from the Department of Biopsychology at Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) examined a cold-blooded reptile using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). The team was looking to answer the question of what happens in a crocodile’s brain when it hears complex sounds. They were able to determine that complex stimuli triggered activation patterns in the crocodile's brain that are similar to those in birds and mammals — a deep insight into evolution.
The results were published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences on April 25, 2018.
Crocodiles count among the most ancient species of vertebrates and have barely changed over the space of more than 200 million years. Accordingly, they constitute a link between dinosaurs and bird species today. "Analyses of crocodile brains thus provide deep insights into the evolution of the nervous system in mammals and may help us understand at which point certain brain structures and behaviours associated therewith were formed," explained Felix Ströckens, who led the research team.
The objective pursued by the team of researchers from Iran, South Africa, France and Germany was to study Nile crocodiles and to ascertain the way sensory information is processed in their brain. To this end, they deployed fMRI - a method that is routinely used in clinical diagnostics and research, but which has never yet been utilized to study a cold-blooded reptile. "In the first step, we had to overcome a number of technical obstacles," said research team member Mehdi Behroozi. "For example, we had to adjust the scanner to the crocodile's physiology, which differs massively from that of mammals in several aspects."
Subsequently, the researchers exposed the animals to various visual and auditory stimuli, including classical music by Johann Sebastian Bach. At the same time, they measured the animals' brain activity. The results have shown that additional brain areas are activated during exposure to complex stimuli such as classical music, as opposed to exposure to simple sounds. The processing patterns strongly resemble the patterns identified in mammals and birds in similar studies.
Consequently, the researchers assume that fundamental neuronal processing mechanisms of sensory stimuli formed at an early evolutionary stage and that they can be traced back to the same origins in all vertebrates.
By successfully deploying fMRI for the examination of a reptile for the first time worldwide, the researchers demonstrated that the method does work for poikilothermic organisms. This non-invasive technology can thus be used for many other species that have not yet been studied in depth.
For more information: www.rspb.royalsocietypublishing.org


 April 24, 2024
April 24, 2024