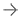Analysis of nontumorous portion of pancreas with or without secondary signs of pancreatic cancer by classification models. Blue outline represents the portion of the pancreas analyzed with classification models. The tumor (red outline) was not identified by the segmentation model; thus, it was not analyzed by classification models. (A) Unannotated CT image in a patient with pancreatic head cancer. (B) Nontumorous portion of the pancreas shows secondary signs of pancreatic cancer (dilation of pancreatic duct with abrupt cutoff [arrowheads]) and was classified as cancerous by the classification models. (C) Nontumorous portion of the pancreas appeared normal and was classified as noncancerous after the dilated duct was replaced and imputed with surrounding normal-appearing pancreas parenchyma.
September 14, 2022 — An AI tool is highly effective at detecting pancreatic cancer on CT, according to a study published in Radiology.
Pancreatic cancer has the lowest five-year survival rate among cancers. It is projected to become the second leading cause of cancer death in the United States by 2030. Early detection is the best way to improve the dismal outlook, as prognosis worsens significantly once the tumor grows beyond 2 centimeters.
CT is the key imaging method for detection of pancreatic cancer, but it misses about 40% of tumors under 2 centimeters. There is an urgent need for an effective tool to help radiologists in improving pancreatic cancer detection.
Researchers in Taiwan have been studying a computer-aided detection (CAD) tool that uses deep learning to detect pancreatic cancer. They previously showed that the tool could accurately distinguish pancreatic cancer from noncancerous pancreas. However, that study relied on radiologists manually identifying the pancreas on imaging.
In the new study, the AI tool identified the pancreas automatically. This is an important advance considering that the pancreas borders multiple organs and structures and varies widely in shape and size.
Tool Has Potential to Detect Smaller Cancers Earlier
The researchers developed the tool with an internal test set consisting of 546 patients with pancreatic cancer and 733 control participants. The tool achieved 90% sensitivity and 96% specificity in the internal test set.
Validation followed with a set of 1,473 individual CT exams from institutions throughout Taiwan. The tool achieved 90% sensitivity and 93% specificity in distinguishing pancreatic cancer from controls in that set. Sensitivity for detecting pancreatic cancers less than 2 centimeters was 75%.
“The performance of the deep learning tool seemed on par with that of radiologists,” said study senior author Weichung Wang, PhD, professor at National Taiwan University and director of the university’s MeDA Lab. “Specifically, in this study, the sensitivity of the deep learning computer-aided detection tool for pancreatic cancer was comparable with that of radiologists in a tertiary referral center regardless of tumor size and stage.”
The CAD tool has the potential to provide a wealth of information to assist clinicians, Dr. Wang said. It could indicate the region of suspicion to speed radiologist interpretation.
“The CAD tool may serve as a supplement for radiologists to enhance the detection of pancreatic cancer,” said the study’s co-senior author, Wei-Chi Liao, MD, PhD, from National Taiwan University and National Taiwan University Hospital.
The researchers are planning further studies. In particular, they want to look at the tool’s performance in more diverse populations. Since the current study was retrospective, they want to see how it performs going forward in real-world clinical settings.
For more information: www.rsna.org


 May 29, 2024
May 29, 2024