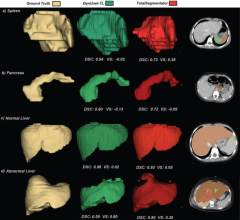
Burton P. Drayer, M.D., chairman, 2009 RSNA Board of Directors
August 31, 2009 - The Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) responds to reaffirmed to a study and accompanying perspective on radiation dose from medical imaging procedures in The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), emphasizing that the potential benefits of medical imaging far outweighs the risk. The Society also stresses how appropriate utilization, low-dose protocols and implementation of programs are lowering dose exposure in medical imaging.
RSNA released a public statement, which included the following:
In "Exposure to Low-Dose Ionizing Radiation from Medical Imaging Procedures," Reza Fazel, M.D., M.Sc., and colleagues reported that imaging procedures are a key source of ionizing radiation exposure in the U.S. and that repeat exams can result in high cumulative doses of radiation. "Elements of Danger - The Case of Medical Imaging," a perspective by cardiologist Michael S. Lauer, M.D., goes beyond that conclusion to assert that most medical imaging exams offer net negative results with little high-level evidence of benefit.
The Fazel article has elicited media and public attention to a topic that many radiology professionals believe should be at the forefront. It is important that one of the salient points from the authors not be overlooked: "An important reason for the growing use of such procedures stems from their ability to radically improve patient care."
There is overwhelming agreement in the radiology community that certain imaging procedures carry risk, but with appropriate utilization, low-dose protocols and implementation of programs that track cumulative dose in the patient's medical record, the potential benefits far outweigh that risk.
Radiologists, medical physicists and other radiology professionals have long recognized that there needs to be conscientious implementation of medical procedures that deliver ionizing radiation and have assumed a collective responsibility for maintaining rigorous standards of practice. Radiologists recognize their responsibility to implement and to follow appropriateness criteria for performing imaging exams. Recent studies have shown that the most significant growth in utilization of imaging procedures has occurred as a result of non-radiologist "self-referral."
In addition to following strict appropriate imaging utilization standards, radiologists and medical physicists have worked together to improve the safety of imaging exams by minimizing dose without sacrificing diagnostic ability. They are directly involved in the development of technologies and protocols to ensure patient safety in medical imaging scenarios. Radiologic scientists are working closely with manufacturers to lower radiation doses to patients without losing image quality.
To increase awareness of cumulative dose and other radiation risks and to explore opportunities to improve patient safety, RSNA has partnered with the American College of Radiology (ACR) to create the ACR/RSNA Task Force for Adult Radiation Protection.
Launched in 2007 by the Alliance for Patient Safety in Pediatric Imaging, the "Image Gently" campaign seeks to raise awareness of pediatric radiation safety and to lower radiation dose in the imaging of children.
While cumulative dose risk remains a significant concern, programs are being initiated to track individual patients' medical imaging procedures and their associated radiation doses. The Radiology and Imaging Sciences at the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center recently announced computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET)/CT equipment purchased by the Clinical Center will be required to routinely record radiation dose exposure in a patient's hospital-based electronic medical record. This represents a significant step to ensure the safety of patients who are exposed to ionizing radiation during imaging tests.
Medical imaging exams are an invaluable tool in the diagnosis and treatment of patients, and radiology professionals will continue to strive to improve the safety of these exams.
For more information: www.rsna.org

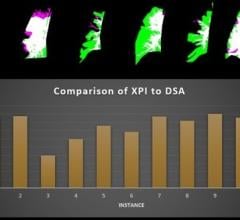
 May 17, 2024
May 17, 2024