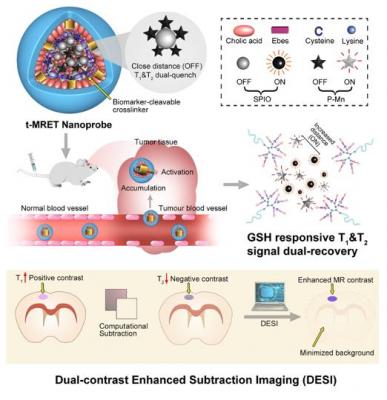
A new technique developed by researchers at UC Davis offers a significant advance in using magnetic resonance imaging to pick out even very small tumors from normal tissue. The team created a probe that generates two magnetic resonance signals that suppress each other until they reach the target, at which point they both increase contrast between the tumor and surrounding tissue. Image courtesy of Xiandoing Xue, UC Davis
May 26, 2020 — Researchers at the University of California, Davis offers a significant advance in using magnetic resonance imaging to pick out even very small tumors from normal tissue. The work was published May 25 in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
Chemical probes that produce a signal on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used to target and image tumors. The new research is based on a phenomenon called magnetic resonance tuning that occurs between two nanoscale magnetic elements. One acts to enhance the signal, and the other quenches it. Previous studies have shown that quenching depends on the distance between the magnetic elements. This opens new possibilities for non-invasive and sensitive investigation of a variety of biological processes by MRI.
The UC Davis team created a probe that generates two magnetic resonance signals that suppress each other until they reach the target, at which point they both increase contrast between the tumor and surrounding tissue. They call this two-way magnetic resonance tuning (TMRET).
Combined with specially developed imaging analysis software, the double signal enabled researchers to pick out brain tumors in a mouse model with greatly increased sensitivity.
"It's a significant advance," said senior author Yuanpei Li, associate professor of biochemistry and molecular medicine at the UC Davis School of Medicine and Comprehensive Cancer Center. "This could help detect very small early-stage tumors."
Two magnetic components
The probe developed by the UC Davis team contains two components: nanoparticles of superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO), and pheophorbide a-paramagnetic manganese (P-Mn), packaged together in a lipid envelope. SPIO and P-Mn both give strong, separate signals on MRI, but as long as they are physically close together those signals tend to cancel each other out, or quench. When the particles enter tumor tissue, the fatty envelope breaks down, SPIO and P-Mn separate, and both signals appear.
Li's laboratory focuses on the chemistry of MRI probes and developed a method to process the data and reconstruct images, which they call double-contrast enhanced subtraction imaging or DESI. But for expertise in the physical mechanisms, they reached out to Professors Kai Liu and Nicholas Curro at the UC Davis Department of Physics (Liu is now at Georgetown University). The physicists helped elucidate the mechanism of the TMRET method and refine the technique.
The researchers tested the method in cultures of brain and prostate cancer cells and in mice. For most MRI probes, the signal from the tumor is up to twice as strong as from normal tissue - a "tumor to normal ratio" of 2 or less. Using the new dual-contrast nanoprobe, Li and colleagues could get a tumor-to-normal ratio as high as 10.
Li said the team is interested in translating the research into clinical use, although that will require extensive work including toxicology testing and scaling up production before they could apply for investigational new drug approval.
For more information: www.


 May 06, 2024
May 06, 2024