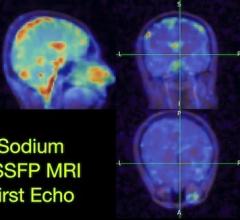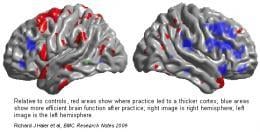
Red areas show where practice led to a thicker cortex blue areas show more efficient brain function after practice. Richard J. Haier, et al. BMC Researcher Notes, 2009.
September 1, 2009 – A study used structural and functional MRI scans to identify increased gray matter in the brain developed after three-months of practicing the video game Tetris.
In the study, “MRI assessment of cortical thickness and functional activity changes in adolescent girls following three months of practice on a visual-spatial task,” published in Biomedical Central (BMC) Research Notes today, researchers at the Mind Research Network used brain imaging and Tetris to investigate whether practice makes the brain efficient because it increases gray matter. Over a three-month period, adolescent girls practiced Tetris, a computer game requiring a combination of cognitive skills. The girls completed both structural and functional MRI scans before and after the three-month practice period, as did girls in the control group who did not play Tetris. A structural MRI was used to assess cortical thickness, and a functional MRI was used to assess efficient activity.
The girls who practiced showed greater brain efficiency, consistent with earlier studies. Compared to controls, the girls that practiced also had a thicker cortex, but not in the same brain areas where efficiency occurred.
Researchers wanted to see if mental practice increased cortical thickness, a sign of more gray matter. If it did, it could be an explanation for why previous studies have shown that mental practice increases brain efficiency. More gray matter in an area could mean that the area would not need to work as hard during Tetris play.
“We showed that practice on a challenging visuospatial task has an impact on the structure of the cortex, which is in keeping with a growing body of scientific evidence showing that the brain can change with stimulation and is in striking contrast with the pervasive and only-recently outmoded belief that our brain’s structure is fixed,” said Dr. Sherif Karama, M.D., a co-investigator at the Montreal Neurological Institute.
Changes in cortical thickness were not where investigators saw more efficiency. Therefore, the manner in which a thicker cortex and increased brain efficiency are related remains a mystery.
The areas of the brain that showed relatively thicker cortex were the Brodmann Area (BA) 6 in the left frontal lobe and BA 22 and BA 38 in the left temporal lobe. Scientists believe BA 6 plays a role in the planning of complex, coordinated movements. BA 22 and BA 38 are believed to be the part of the brain active in multisensory integration-or our brain’s coordination of visual, tactile, auditory, and internal physiological information.
Functional MRI (fMRI) showed greater efficiency after practice mostly in the right frontal and parietal lobes including BAs 32, 6, 8, 9, 46 and BA 40. These areas are associated with critical thinking, reasoning, and language and processing.
According to the researchers, Tetris was a useful tool for brain research. Tetris is apparently complex for the brain, requiring many cognitive processes such as attention, hand/eye co-ordination, memory and visual spatial problem solving all working together very quickly. A number of previous scientific studies also have used Tetris.
The researchers chose to use adolescents in this study because it is more likely to see changes in developing brains. Girls were chosen because boys tend to have considerably more computer game experience and, therefore, may not show detectable brain change after game practice. All 26 girls in the study had limited computer game experience.
BMC Research Notes is a peer-reviewed, open access online journal.
For more information: www.biomedcentral.com/bmcresnotes/


 December 15, 2025
December 15, 2025