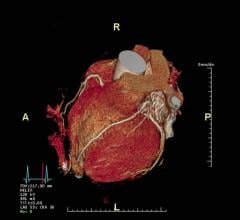
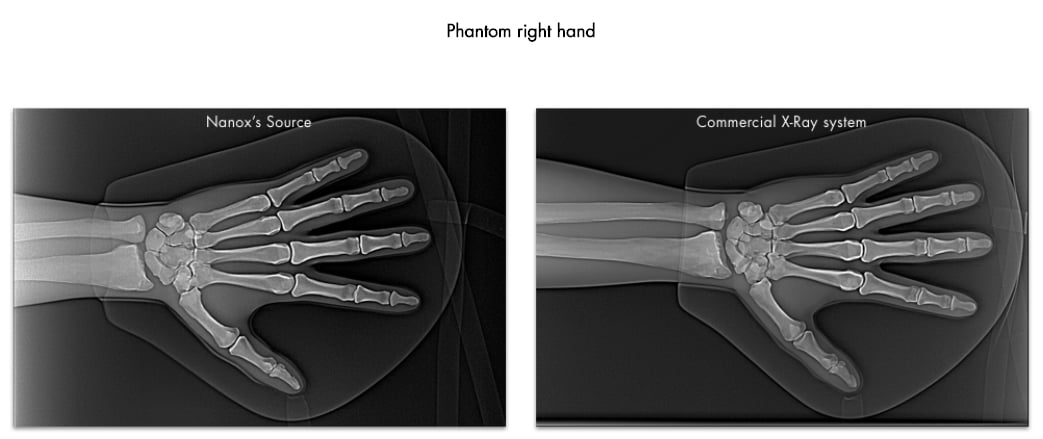
The Nanox.ARC next-generation cold cathode X-ray prototype at the 2020 Radiology Society of North America (RSNA) virtual meeting. The live demonstration featured a range of 2-D and 3-D imaging procedures using its groundbreaking digital X-ray tube in a unique multi-source array structure.
December 3, 2020 — Nanox said today it successfully demonstrated its Nanox.ARC next-generation cold cathode X-ray prototype at the 2020 Radiology Society of North America (RSNA) virtual meeting. The live demonstration featured a range of 2-D and 3-D imaging procedures using its groundbreaking digital X-ray tube in a unique multi-source array structure.
Modern X-ray equipment is said to have been digitalized. However, this change has only affected the image capturing, processing and data storage section - not the actual X-ray tube itself. At the heart of every new X-ray tube, there still is a metal filament that has gone virtually unchanged for the past 100 years.
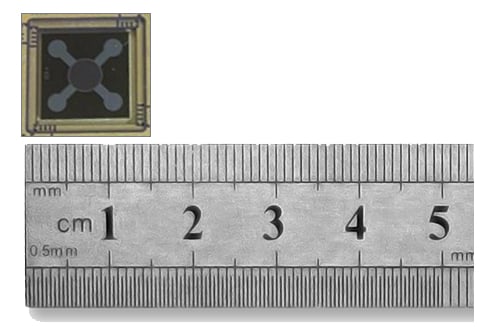 Nanox has developed a silicon chip which operates as a field-emission-type cathode, or "cold cathode." A cold cathode extracts electrons from metal by applying an external electric field rather that large amounts of heat to create a an electron beam. Using proprietary micro-electrical-mechanical-systems (MEMS) techniques, the Nanox chip contains millions of nanoscale gates in a single chip, about one square centimeter in size. A very high electric field is induced at the nanoscale gap between the cone emitters and the hole right above them (called the "gate hole"). The high electric field is highly effective at extracting electrons from the cone emitters. These electrons make up the electron beam between the cathode and the anode.
Nanox has developed a silicon chip which operates as a field-emission-type cathode, or "cold cathode." A cold cathode extracts electrons from metal by applying an external electric field rather that large amounts of heat to create a an electron beam. Using proprietary micro-electrical-mechanical-systems (MEMS) techniques, the Nanox chip contains millions of nanoscale gates in a single chip, about one square centimeter in size. A very high electric field is induced at the nanoscale gap between the cone emitters and the hole right above them (called the "gate hole"). The high electric field is highly effective at extracting electrons from the cone emitters. These electrons make up the electron beam between the cathode and the anode.
“We are pleased to have now demonstrated a working prototype of our next generation digital X-ray technology, the Nanox.ARC, in a range of medical imaging procedures that produced unique clinical value. We believe the Nanox.ARC has the potential to significantly expand the market by providing access to the roughly two-thirds of the world’s population who currently do not have access to medical imaging. If successful, we believe this can revolutionize preventive healthcare through early detection of serious and costly medical conditions," explained Ran Poliakine, chairman and CEO of Nanox. "To date, we have signed agreements for the deployment of more than 5,100 Nanox.ARC units through our service providers in numerous countries, and, pending local regulatory approvals and customer acceptance, we believe we can begin deployments as early as mid-year 2021.”
Development of Cold-cathode X-ray Tube Technology
Field Emission Technologies, a Sony spin-off company, developed the technical know-how to produce the world's first high-quality FED (Field Emission Display) panel. While the cold cathode principle was not new to scientific researchers, they battled to obtain ample and stable electrons in a non-heat driven emission platform. Nanox had acquired this technology and ported it to the medical imaging field.
In the medical imaging sector, using a field-emission-type X-ray tube has several desirable properties:
1. Rapid time switching: In a hot cathode, the acceleration of the electrons towards the Anode (thereby creating X-rays) is done by activating and switching a high voltage supply. This process takes time (on the order of milliseconds). In a cold cathode, one can set the high voltage and switch only the gate voltages – a process that can take only microseconds.
2. Rapid intensity change: The Field Emitter current depends on the applied voltage, and the X-ray intensity depends on the Field Emitter current. With cold cathode technology, it is possible to uncouple these two parameters, i.e., the current's power is independent of the voltage. Thus, the X-ray intensity can be rapidly controlled by increasing the speed of switching or by creating short pulses.
3. Colder Mechanism: Electrons are extracted from the metal cathode by an applied electric field, while the emitter temperature is significantly lower than that of Hot Cathode (thermionic emission) filaments. Hot cathode temperature is over 2000 degrees Celsius while a Cold Cathode temperature is that of room temperature.
4. Lifetime improvement: A colder cathode has the benefits of a longer lifetime. The hot cathode's longevity is of thousands of patients' lifetime, whereas that of the Cold Cathode is more than 1 million patients' lifetime.
Up until now, Cold Cathodes, including CNT (or Carbon Nano Tube) and standard Spindt cathodes, failed to achieve the quality level, efficiency, and the lifetime required for commercial products.
Over nine years of development by a Japanese and Israeli engineering team, produced a stable cold-cathode field emission MEMS silicon.
The company hopes to create an inexpensive, low-energy consumption, lightweight, non-heat generating X-ray system that will be easily used by clinics, especially in developing countries.
For more information: www.nanox.vision


 April 23, 2024
April 23, 2024