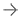July 31, 2017 — GE Healthcare announced that it has licensed computed tomography (CT) organ dosimetry technology developed at Duke University. The technology enables automatic calculation of organ dose, helping the clinician to better estimate the radiation exposure to the patient. The automatic calculation reduces the time needed to perform assessments for large numbers of patients, enabling epidemiologic and dose trend analysis studies.
“This technology assesses organ doses in patients undergoing CT in an examination-specific manner, where granular dose estimates are precisely informed by the patient anatomy and the exact irradiation condition,” said Ehsan Samei, a professor of radiology, physics and biomedical engineering at Duke, who led development of the tool. “The technology includes a realistic estimation of variability associated with the dose estimates, raising the confidence in the reported values.”
The technology will be incorporated into an organ dose module within GE’s DoseWatch, a digital informatics solution that automatically collects, monitors and reports on radiation dose indices for diagnostic imaging exams. DoseWatch is used by healthcare providers around the world to reduce variation in practice, help ensure patient safety, and drive compliance with government regulations and accreditation requirements. DoseWatch will provide the CT study acquisition information for the organ dose calculation, as well as the machine-learning technology to accurately match a patient with his or her electronic counterpart.
Duke’s technology employs a unique convolution-based approach to organ dose and leverages the XCAT phantom library, a collection of more than 400 highly detailed computational phantoms for adult men, women, pediatric and pregnant patients. The XCAT library is referenced in over 100 peer-reviewed articles.
Duke has published previously on the convolution-based estimation of organ dose. GE and Duke presented jointly at the 2016 Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) annual meeting on a generalized framework for organ dose monitoring for CT.
For more information: www.gehealthcare.com

 May 15, 2024
May 15, 2024