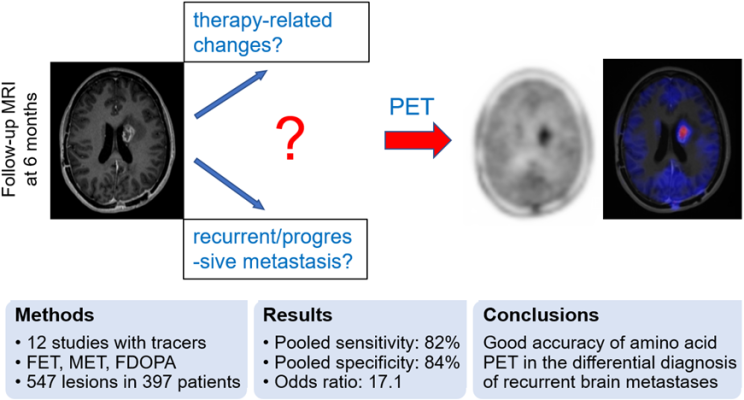
Graphical Abstract. Does a new or increasing contrast enhancement on T1 MRI represent a consequence of treatment or progressive/recurrent tumor? This common clinical dilemma can be resolved by amino acid PET with good diagnostic accuracy.
May 12, 2023 — A newly published meta-analysis indicates that amino acid PET can accurately differentiate recurrent or progressive brain metastases from treatment-related changes. A specificity of 84 percent suggests that it may reduce the number of invasive procedures and overtreatment in patients who in fact experience treatment-related changes. This research was published in the May issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Brain metastases occur in 20 to 40 percent of all cancer patients and are most likely to occur in those with lung, breast and renal cancer, melanoma, and cancers of the gastrointestinal tract. Management of patients with brain metastases usually includes surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Some patients develop treatment-related changes such as radiation necrosis or pseudoprogression.
“A differentiation between recurrent or progressive brain metastases and treatment-related changes is challenging,” said Igor Yakushev, senior physician in the department of nuclear medicine at Technical University of Munich in Germany. “As the management of patients with recurrent or progressive brain metastases and treatment-related changes is fairly different, accurate and early differential diagnosis is essential.”
The meta-analysis included 12 studies with amino acid PET radiotracers. The studies included a total of 397 patients with 547 lesions. Overall, 269 lesions (49 percent) were found to be recurrent or progressive brain metastases. Using a histologic examination and/or radiological and clinical follow-up as reference, pooled sensitivity and specificity of amino acid PET were found to be 82 and 84 percent respectively.
“This study provides IIa class evidence on diagnostic utility of amino acid PET in the differential diagnosis of recurrent or progressive brain metastases,” stated Yakushev. “These findings are in line with an increasing role of molecular imaging in the management of patients with brain tumors, yet the results also point to potential for further improvement of diagnostic accuracy.”
For more information: www.snmmi.org


 May 17, 2024
May 17, 2024 



![(A) PET images of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-ZCAM241 uptake at baseline and 3, 7, and 12 days after injection as inflammatory arthritis developed in single representative individual mouse. Images are normalized to SUV of 0.5 for direct comparison between time points. (B) CD69 immunofluorescence Sytox (Thermo Fisher Scientific) staining of joints of representative animals during matching time points.](/sites/default/files/styles/feed_medium/public/PET%20Tracers.jpeg?itok=P5Di6MIe)