MR-guided focused ultrasound (MRgFUS) ablation is a noninvasive technique that requires no incision or puncture to perform. Instead, it uses the acoustic energy from high-intensity focused ultrasound to remove, or ablate, diseased tissue. Continuous MRI is used to locate the lesions and monitor the temperature change during the ablation process.
Primary advantages of MRgFUS over other breast cancer treatments are that it is a noninvasive, outpatient procedure offering a quick recovery time, and that it provides precise measurement of temperature changes during the procedure.
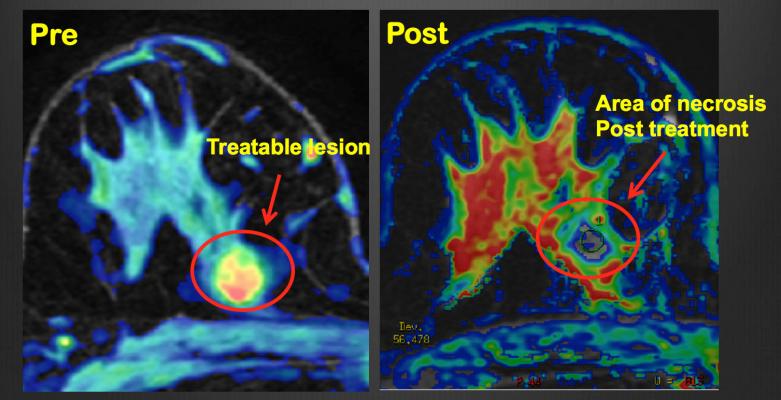
"In the treatment stage, we are able to precisely visualize where the energy is having an effect and to measure exactly the rise in temperature," said Alessandro Napoli, M.D., Ph.D., assistant professor of radiology, Sapienza University, Rome. "Temperature monitoring is particularly important, since too low a temperature is ineffective and too high a temperature may be dangerous."
Napoli and colleagues assessed the safety and efficacy of MRgFUS in 12 patients with invasive ductal breast cancer before surgical removal of the cancer and biopsy of the lymph nodes. They used 3T MRI to confirm the presence and treatable location of cancerous lesions. The patients then underwent single-session MRgFUS treatment. Researchers evaluated treatment efficacy through post-surgery pathology.
None of the patients experienced significant complications during or immediately after the procedure. In 10 of the 12 patients, MRI showed no enhancement in the treatment area after the procedure. Post-surgery histological evaluation confirmed the absence of residual disease in the treatment area in those 10 patients.
"This procedure allows for safe ablation of breast cancer," said Napoli. "At pathology, no significant viable tumor was found in the specimens from these 10 patients."
In the other two cases, treatment failed due to transducer malfunction, and the pathologist observed residual tumor in the samples.
According to Napoli, MRI guidance is crucial for correct identification of lesions, treatment planning and real-time control during the procedure. Specifically, monitoring with MRI allows for efficient deposit of energy into the region of treatment at the correct range of between 60 degrees and 70 degrees Celsius (approximately 140 to 158 degrees Fahrenheit).
"This is carried out by a special sequence that is called MR thermometry," said Napoli. "Only MRI presently has the ability to determine, in real time, fine temperature quantification."
While the initial results are promising, Napoli said more research will be needed before the approach can be adopted as a stand-alone treatment for breast cancer.
Co-authors are Luisa Di Mare, M.D., Federica Pediconi, M.D., Michele Anzidei, M.D., Vincenzo Noce, M.D., and Carlo Catalano, M.D.