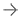
Medical imaging artificial intelligence (AI) company Annalise.ai has announced that results from a pioneering clinical study, which examined whether its technology improves radiologists’ performance, have been published in the journal European Radiology. Image courtesy: Annalise ai
September 20, 2023 — Medical imaging artificial intelligence (AI) company Annalise.ai has announced that the results from a pioneering clinical study, which examined whether its comprehensive diagnostic support technology improves radiologists’ performance, have been published in the journal European Radiology.
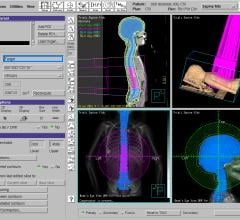
The multi-reader, multi-case study, “Effects of a comprehensive brain computed tomography deep learning model on radiologist detection accuracy,” compared how accurate 32 radiologists were at detecting clinical findings on non-contrast CT brain scans with and without the aid of Annalise’s deep-learning system, Annalise Enterprise CTB. The results, according to an announcement released by company, showed radiologists assisted by Annalise Enterprise CTB achieved significantly higher detection accuracy than unassisted radiologists. They also interpreted cases significantly faster than unassisted radiologists. It further noted the new research validates the precision of the solution on Head NCCTs, helping improving TAT for time-sensitive conditions.
The study demonstrated Annalise’s AI solution improved radiologists' accuracy by 32% and reduced their overall reading time by 11%, reported the Australian-based company, adding that the findings suggest utilizing the Annalise model could have several benefits, including reduced error rates, enhanced efficiency, and improved triage, thereby facilitating the provision of timely, effective patient care.
Non-contrast computed tomography of the brain (NCCTB) is frequently used to detect intracranial pathology. However, the results of these complex scans are subject to interpretation errors. Annalise Enterprise CTB is designed by and for clinicians, acting like a second pair of eyes to assist with scan interpretation. It can detect up to 130 findings on unenhanced CT brain scans in under two minutes, including numerous conditions such as stroke or intracranial bleeds that require time-sensitive interventions.
“This important clinical study indicates that radiologist performance improves with diagnostic support from a comprehensive, multi-finding AI solution,” said Annalise Chief Medical Officer Rick Abramson, MD, MHCDS, FACR. He added, “The results have important implications for patients and clinicians. We look forward to further measuring and validating them in the clinical trials we continue to conduct around the world.” The announcement noted that this paper adds to growing evidence showing that the Annalise Enterprise CTB solution improves radiologist detection speed and accuracy.
In this study, radiologists first analyzed the cases without using the Annalise Enterprise CTB solution. After a "wash-out" period of at least four months, the same radiologists re-evaluated these cases with assistance from the Annalise CTB solution. Differences in area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) and Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) were quantified using a ground-truth gold standard. The Annalise solution significantly improved radiologists’ accuracy for 91 findings and was comparable to that of the radiologists for the remaining findings.
Reference:
Buchlak Q et al. Effects of a comprehensive brain computed tomography deep learning model on radiologist detection accuracy. Eur Radiol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-023-10074-8
More information: www.annalise.ai


 May 08, 2024
May 08, 2024