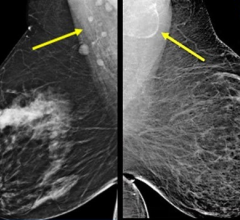
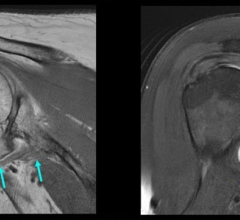
September 29, 2010 — In a prospective study published in the European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, researchers at Boca Raton Regional Hospital, Boca Raton, Fla., showed that positron emission mammography (PEM) and breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) had a comparably high ability to detect cancerous lesions.
The prospective study enrolled 182 women with recent biopsy-proven primary breast cancer. It also found that PEM was not impacted by menopausal status, breast density or hormone replacement therapy, making PEM a valuable alternative.
PEM scanners are high-resolution breast positron emission tomography (PET) systems that show the location as well as the metabolic phase of a lesion. The metabolic view assists physicians to make the optimal cancer care decision by providing an unprecedented ability to distinguish between benign and malignant lesions, what researchers term “specificity.” PEM is different from X-ray mammography in that it is currently not used as a screening modality, rather is deployed to confirm extent of disease in a patient already diagnosed with a primary breast cancer.
“We were very pleased to find that PEM and MRI had comparable ability to detect cancerous lesions regardless of type or severity of the tumor,” said Kathy Schilling, M.D., lead author on the study. “In addition, the data showed that PEM is a fantastic alternative for women with dense breasts or where timing of an MRI due to menstrual cycle is challenging. The next step is to understand how PEM and MRI compare when differentiating between benign and malignant suspicious lesions.”
Results from a separate NIH-sponsored clinical study (NIH Grant 5R44CA103102), recently presented at the 2010 Society of Nuclear Medicine Annual Meeting, comparing PEM and breast MRI help answer Dr. Schilling’s question. The multi-site study of hundreds of women with newly diagnosed breast cancer shows that PEM demonstrated a 6 percent improvement in specificity, ability to differentiate between malignant and benign lesions, suggesting that PEM may reduce unnecessary biopsies. These results are particularly significant for women who cannot tolerate an MRI exam and require an alternate imaging tool. The study is slated for publication in the December issue of the journal Radiology.
For more information: naviscan.com
© Copyright Wainscot Media. All Rights Reserved.
Subscribe Now

 May 17, 2024
May 17, 2024