June 23, 2016 — The triggers of autoimmune inflammation in multiple sclerosis (MS) have eluded scientists for many years, but molecular imaging is bringing researchers closer to identifying them, according to a new study. Molecular imaging is also providing a means of evaluating next-generation therapies for MS, said researchers introducing the study at the 2016 Annual Meeting of the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI), June 11-15 in San Diego.
More than 2.3 million people are affected by MS worldwide, according to estimates from the National Multiple Sclerosis Society. MS is marked by inflammation and the systematic destruction of neuronal fibers, specifically myelin, in the nervous system. Myelin is the fatty layer that both protects the fibers and increases the speed of signaling along the axon of nerve cells. Similar inflammatory processes are typical in the pathology of other neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, gastrointestinal diseases like Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis, and the vascular inflammation that leads to atherosclerosis.
“Inflammation is the body’s physiological defense to harmful stimuli and it plays a critical role in the immune response to injury and infection,” said senior investigator, Zhude Tu, Ph.D., professor of positron emission tomography (PET) radiochemistry at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Mo. “However, despite the benefits of acute inflammation in promoting healing, these same processes are associated with numerous pathological conditions when chronic inflammation is left unchecked.”
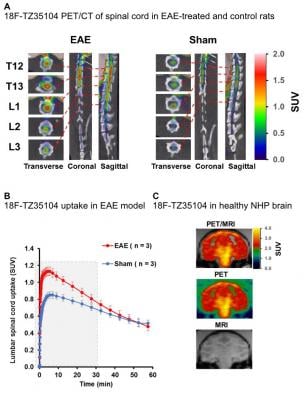
This study furthers a growing body of research pointing to a process called sphingolipid signaling as a primary mechanism in inflammatory disease processes. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval in 2010 of fingolimod for relapsing MS further supports the hypotheses that the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1) is an ideal biomarker for imaging and new therapies. Fingolimod works by turning down the autoimmune response via immune cell S1P1.
First author of the study Adam J. Rosenberg, Ph.D., and his colleagues produced a library of S1P1-targeted small molecules and radiolabeled them with fluorine-18. These radiotracers bind directly to S1P1 receptors and can be imaged with preclinical PET, through noninvasive methodology to investigate the physiological functions of S1P1 receptors in animal models as a precursor for human studies. In this case, researchers imaged S1P1 in rodent models of inflammatory disease and healthy controls. They found that the PET imaging agents not only were able to detect an increase in S1P1 expression in animals with an inflammatory response when compared to healthy controls, but that the compounds also crossed the blood brain barrier in healthy animals, a significant limiting factor in the development of central nervous system drugs.
“These compounds represent promising PET tracers for imaging MS and other inflammatory diseases by quantitative assessment of S1P1 expression in the body,” said Tu.
For more information: www.snmmi.org


 May 17, 2024
May 17, 2024