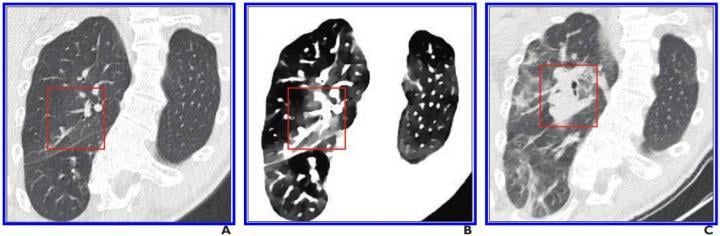
A, Initial conventional axial CT image shows no noticeable lung damage (within red box) in right upper lobe. B, Electron density spectral CT image obtained at same time as image in A shows lesions (within red box) in right upper lobe. C, Follow-up conventional axial chest CT image obtained 5 days after images in A and B confirm presence of lesions (within red box) in right upper lobe. Image courtesy of the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS), American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR)
October 22, 2020 — According to an open-access article in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), the use of spectral computed tomography (CT) with electron density imaging could improve the assessment of lung lesion extent in patients with early-stage coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
"In the present study," wrote Beatrice Daoud and colleagues at Antony's Private Hospital in France, "we report the first retrospective data from the spectral chest CT findings of patients with reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)-confirmed COVID-19 (i.e., patients with positive RT-PCR test results)."
Since March 17, 2020, every patient who has had CT performed at the authors' institution for either suspected or RT-PCR-confirmed COVID-19 has undergone dual-layer detector-based spectral CT (IQon Spectral CT, Philips Healthcare). To evaluate the potential benefit of spectral imaging--electron density imaging, especially--two experienced thoracic radiologists reviewed the cases of four patients who each underwent two chest CT scans for confirmed COVID-19. Reconstructing the spectral CT images using the same standard soft kernel (filter B) and a similar iterative method that was used to acquire the conventional CT images, Daoud's team also compared initial conventional CT images with follow-up conventional CT images.
In all four patients, their pulmonary lesions (45 ground-glass opacities, overall) were more conspicuous on electron density images than on initial conventional CT images and were clearly confirmed on follow-up conventional CT images. Moreover, lesion extent, assessed via semiquantitative reporting scale denoting surface area involvement for each lobe, was easier to ascertain on electron density images. With Daoud and colleagues' results indicating electron density imaging improves early assessment of the extent of ground-glass opacities that could be missed by conventional CT, electron density showed the most promising results by enhancing the contrast of ground-glass opacities compared with the normal lung.
"We reviewed conventional chest CT images obtained with a parenchyma kernel and standard lung window setting, as is usually the case in everyday radiology practice," Daoud et al. explained, adding that they compared these images with conventional images obtained using a soft mediastinum kernel and standard lung window setting, conventional images obtained using a soft mediastinum kernel and narrow lung window setting, virtual low-monoenergy images, virtual high-monoenergy images, and electron density images.
"Our results suggest that the better ground-glass opacity visualization obtained using electron density imaging may be chiefly related to the increased visual noise in the image with soft kernel reconstruction and narrow lung window setting compared with electron density imaging, for which narrowing the window does not impair image quality," the authors of this AJR article concluded.
For more information: www.arrs.org
Related Coronavirus Content:
How COVID-19 Appears on Medical Imaging — Photo Gallery
VIDEO: Imaging COVID-19 With Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS)
Cardiac Imaging Best Practices During the COVID-19 Pandemic
RSNA Publishes COVID-19 Best Practices for Radiology Departments
ASE Guidelines for the Protection of Echocardiography Providers During the COVID-19 Outbreak
New CT Scoring Criteria for Timely Diagnosis, Treatment of Coronavirus Disease
FDA Issues New Policy for Imaging Systems During COVID-19
VIDEO: COVID-19 Precautions for Cardiac Imaging — Interview with Stephen Bloom, M.D.
A Review of Studies Cautions Against Chest CT for Coronavirus Diagnosis
New Research Finds Chest X-ray Not Reliable Diagnostic Tool for COVID-19
VIDEO: Radiology Industry Responding to COVID-19
University of Washington Issues Radiology Policies for COVID-19
VIDEO: Best Practices for Nuclear Cardiology During the COVID-19 Pandemic — Interview with Hicham Skali, M.D.
New Research Highlights Blood Clot Dangers of COVID-19
Survey Reveals Most Medical Practices are Now Using Telehealth Due to COVID-19
CMS Offers Recommendations on Reopening Healthcare in Areas of Low COVID-19 Cases
CT Provides Best Diagnosis for Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19)
Radiology Lessons for Coronavirus From the SARS and MERS Epidemics
Radiologists Describe Coronavirus CT Imaging Features
CT Imaging of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Pneumonia
ACC COVID-19 recommendations for the cardiovascular care team
VIDEO: What Cardiologists Need to Know about COVID-19 — Interview with Thomas Maddox, M.D.


 April 22, 2024
April 22, 2024