May 29, 2018 — A team of researchers including investigators from Mayo Clinic has identified a technology to address the problem of false positives in computed tomography (CT)-based lung cancer screening. The team’s findings are published in the current issue of PLOS One.
“As physicians, one of the most challenging problems in screening patients for lung cancer is that the vast majority of the detected pulmonary nodules are not cancer,” said Tobias Peikert, M.D., a pulmonologist at Mayo Clinic. “Even in individuals who are at high risk for lung cancer, up to 96 percent of nodules are not cancer.”
Peikert said false-positive test results cause significant patient anxiety and often lead to unnecessary additional testing, including surgery. “False-positive lung cancer screening results also increase healthcare costs and may lead to unintentional physician-caused injury and mortality,” Peikert said.
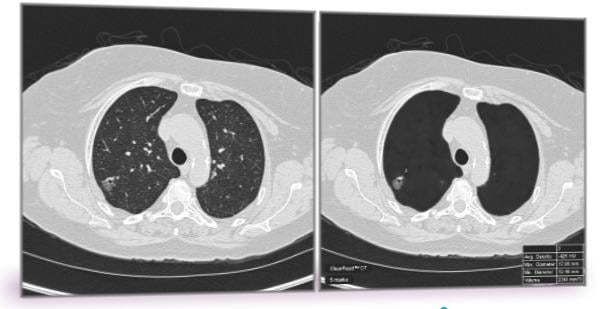
To address the problem of false positives in lung cancer screening, Peikert and Fabien Maldonado, M.D., from Vanderbilt University, along with their collaborators, used a radiomics approach to analyze the CT images of all lung cancers diagnosed as part of the National Lung Cancer Screening Trial. Radiomics is a field of medicine that involves extracting large amounts of quantitative data from medical images and using computer programs to identify disease characteristics that cannot be seen by the naked eye.
Researchers tested a set of 57 variables for volume, nodule density, shape, nodule surface characteristics and texture of the surrounding lung tissue. They identified eight variables which enabled them to distinguish a benign nodule from a cancerous nodule. None of the eight variables were directly linked to nodule size and the researchers did not include any demographic variables such as age, smoking status and prior cancer history as part of their testing.
Peikert said that while the technology looks very promising and has the potential to change the way physicians evaluate incidentally detected lung nodules, it still requires additional validation.
Funding for this research was provided by the Department of Defense, in collaboration with Vanderbilt University School of Medicine.
For more information: www.journals.plos.org/plosone
Related Lung Cancer Content
Artificial Intelligence Improves Lung Cancer Detection
ACR Urges Stricter Adherence to Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines

 April 16, 2024
April 16, 2024