August 9, 2018 — In metastatic breast cancer, prognosis and treatment is largely influenced by estrogen receptor (ER) expression of the metastases. However, little is known about ER expression across metastases throughout the body and surrounding normal tissue. Using a positron emission tomography (PET) tracer, researchers in the Netherlands have been able to identify differences in ER expression, which could help guide treatment for metastatic breast cancer patients. The study is featured in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine’s August issue.
According to the American Cancer Society, breast cancer is the most common cancer in American women, except for skin cancers, and it is the second leading cause of cancer death for women (following lung cancer). Currently, the U.S. has more than 3.1 million breast cancer survivors, and American women have a 1 in 8 chance of developing breast cancer.
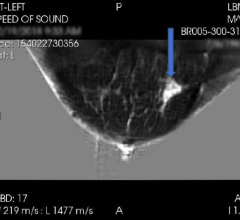
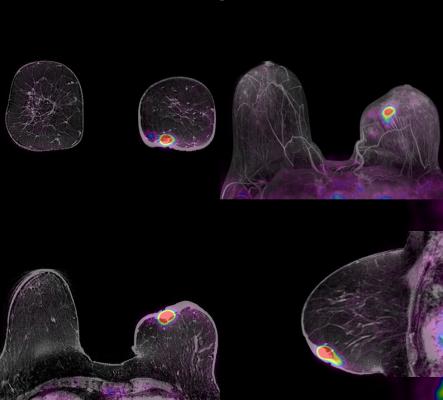
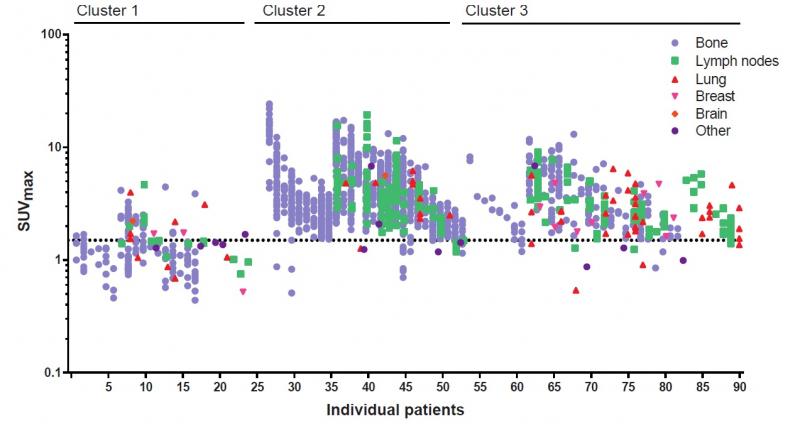
For the study, researchers used fluorine-18-fluoroestradiol (18F-FES) PET to assess ER expression heterogeneity in 91 patients with metastatic breast cancer. 18F-FES uptake was analyzed in 1,617 metastases, as well as in normal tissue.
“The results showed that approximately 50 percent of the patients had one or more estrogen-receptor negative lesions, while the primary tumor was estrogen-receptor positive,” explained Geke A.P. Hospers, M.D., Ph.D., professor of medical oncology at the University of Groningen in The Netherlands. “This heterogeneity of ER expression is, therefore, really common, and it likely affects treatment outcome.”
A higher uptake was found in bone metastases compared to lymph nodes and lung metastases. In addition, in this largest study so far to examine background 18F-FES uptake in the normal tissue surrounding each organ, background uptake was also found to vary per organ, with uptake highest in the skeleton.
Hospers pointed out, “We concluded that 18F-FES uptake in both tumor and normal tissue uptake is heterogeneous and influenced by the site of metastasis. By using cluster analysis on imaging characteristics and metastatic site, three distinct patterns of patients with ER positive metastatic breast cancer were identified.”
She explained the significance, stating, “ER negative lesions will not respond to endocrine treatment, but other ER positive lesions may. The knowledge of this heterogeneity by means of 18F-FES PET may support future specific treatment of metastasis. For example, one ER negative lesion could be treated by radiotherapy, while the endocrine treatment is continued for the other ER positive lesions. The three distinct patterns in ER positive metastatic breast cancer that we identified with our analysis might be useful for future stratification in intervention studies and optimizing personalized treatment.”
For more information: www.jnm.snmjournals.org
Reference


 April 18, 2024
April 18, 2024