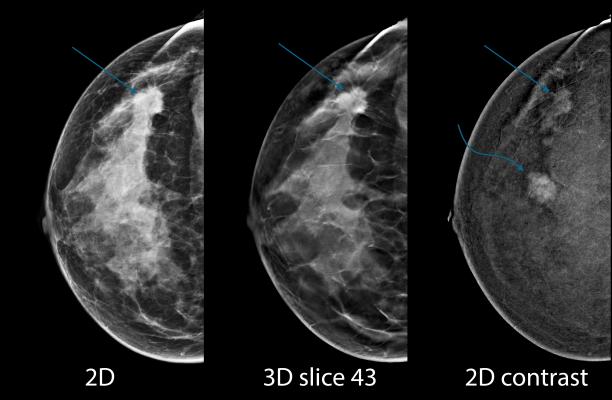
February 22, 2017 — A new digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) technique has the potential to reduce the rate at which women are called back for additional examinations without sacrificing cancer detection, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
In 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved DBT for use with full-field digital mammography (FFDM) in breast imaging. DBT uses a scanner that rotates partially around the breast, providing individual images of thin layers of tissue. When used with FFDM, DBT has been shown to improve cancer detection and reduce callbacks for additional examinations. However, the combination of the two methods requires a second radiation exposure to the breast, while also slightly increasing the time a patient spends in breast compression.
Researchers at Christiana Care Health System’s Helen F. Graham Cancer Center & Research Institute in Newark, Del., have been exploring a relatively new approach in which the DBT images are used to create a synthesized 2-D (s2D) compilation image. The method has the potential to render FFDM unnecessary.
“The adoption of s2D mammography combined with DBT into screening programs would limit radiation exposure to the patient, and, on the basis of our results, may improve clinical performance,” said Jacqueline S. Holt, M.D., FACR, director of breast imaging at Christiana Care Health System’s Helen F. Graham Cancer Center & Research Institute.
Holt and colleagues set out to compare the clinical performance of DBT-s2D with that of DBT-FFDM and FFDM alone. As part of a community oncology program dedicated to breast imaging, the researchers were able to study 78,810 screening mammograms performed from 2011 to 2016. In the study group, 32,076 women were screened with FFDM, 30,561 women were screened using DBT-FFDM, and 16,173 women were screened using DBT-s2D. Performance was assessed by looking at recall rate, the cancer detection rate and positive predictive value (PPV), or the ability to predict if an image-detected abnormality is cancer.
DBT-s2D’s recall rate was only 4.3 percent, compared with 5.8 percent for DBT-FFDM. Overall cancer detection rates were similar, but DBT-s2D detected 76.5 percent of invasive breast cancers, compared with 61.3 percent for DBT-FFDM. At 3.6 percent, the false positive rate for DBT-s2D was significantly lower than the 5.2 percent rate for DBT-FFDM. And the positive predictive value of biopsy for DBT-s2D was 40.8 percent, compared to 28.5 percent for DBT-FFDM.
Holt described the findings as both encouraging and surprising, especially given the fact that, with DBT-s2D, the positive predictive value went up.
“If synthesized 2-D imaging is performed, you’ll get equal or better patient outcomes and go to a lower radiation dose,” she said. “These findings could be a practice-changer globally.”
The results of the study also suggest that adoption of s2D mammography combined with DBT into screening programs would reduce the number of false-positive findings — an important consideration in the age of value-based medicine.
“The downstream cost reduction when women don’t need to be called back for additional imaging amounts to millions of healthcare dollars saved,” Holt said.
Holt understands that radiologists may be wary of relying on the s2D image. Her advice for clinics is to gradually adopt the technology and track how they’re doing through an initial trial period during which the DBT-s2D approach is used side-by-side with the DBT-FFDM technique.
“A lot of the controversy surrounding screening mammography is about false-positive findings,” Holt said. “With this method, we are addressing this issue, optimizing patient care and adding value.”
For more information: www.pubs.rsna.org/radiology
References
Holt, J.S., Aujero, M.P., Gavenonis, S.C., Benjamin, R., et al. “Clinical Performance of Synthesized Two-dimensional Mammography Combined with Tomosynthesis in a Large Screening Population,” Radiology. Published online Feb. 21, 2017. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2017162674

 April 15, 2024
April 15, 2024