Dave Fornell is the editor of Diagnostic & Interventional Cardiology magazine and assistant editor for Imaging Technology News magazine.
Key Technology Trends in Radiation Therapy at ASTRO 2018
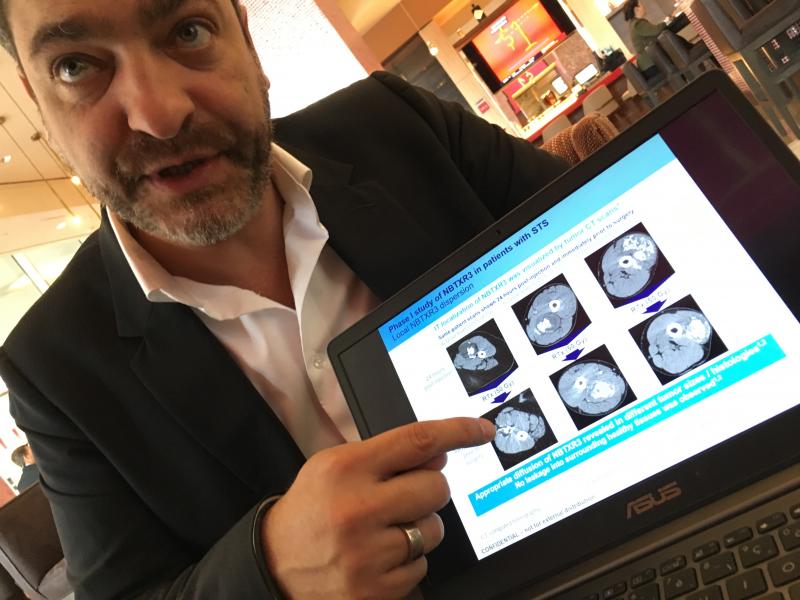
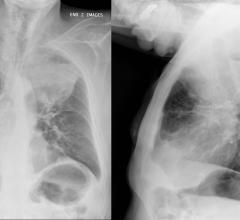
Laurent Levy, CEO of Nanobiotix, explains the use of his company's nanoparticles to enhance the radiation sensitivity of tumor tissue to improve patient outcomes. The images show the initial tumor and enhancement areas due to the nanoparticles and the resulting outcomes following treatment.
Here are a few of the radiation oncology technology advancement takeaways seen at the 2018 American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) annual meeting in October.
To see some of the newest technologies displayed on the expo floor, watch the VIDEO "Editor's Choice of the Most Innovative Radiation Oncology Tech at ASTRO 2018."
Artificial Intelligence to Aid Treatment Planning
Artificial intelligence (AI) was one of the big topics discussed in sessions and on the ASTRO 2018 show floor. ASTRO also had numerous sessions on the application of AI and how it may aid several areas for research and speeding workflow. Sessions included discussion for deep learning applications in treatment planning, clinical decision support, automated image-guided adaptive radiation therapy and how it can aid in genomic/radio-biologic data mining. AI is being developed to help automate treatment planning software and cut the time it takes to develop plans from hours or days, down to minutes.
In early 2018, Mirada Medical received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 510(k) clearance for world’s first AI-powered auto-contouring solution. The DLCExpert software is used for automatic contouring of computed tomography (CT) scans based on next-generation deep learning contouring (DLC) is now in use in multiple academic medical centers worldwide. The vendor highlighted this technology at ASTRO 2018.
Examples of AI auto-segmentation and contouring were also demonstrated by RaySearch and examples of AI-automated plans where shown in sessions. See an example of this AI technology in the Editor's Choice VIDEO.
On the ASTRO show floor I ran into Steve Jiang, Ph.D., director of the medical artificial intelligence (AI) and automation lab and vice-chair of the Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Texas Southwestern. He is one of the top experts on how AI is being integrated in radiation therapy. Watch an interview with him in the VIDEO "The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Radiation Therapy."
Another expert in the field is Kevin Moore, Ph.D., DABR, deputy director of medical physics and associate professor, University of California San Diego. We spoke at AAPM in July about his daily clinical use of an artificial intelligence treatment planning software. Watch an interview with Moore in the VIDEO "Real-world Implementation of Deep Learning for Treatment Planning."
Improving Radiosensitivity and Personalizing Radiation Dose
Radiation oncology has largely had a one-size-fits-all mentality in treating patients, but patients' healthy cells and their cancerous tumor cells can greatly vary in their sensitivity and response to radiation therapy. ASTRO had numerous sessions on research efforts to better tailor therapies to each patient to cause less collateral damage to health tissues and more damage to cancer. This includes the use of radiomics (the study of small radiology image features to find commonalities to better risk stratify patients), genomics (the study of the genetic profiles for both patients and cancer cells) and liquid biopsy blood tests to capture circulating tumor cells and eliminate the need for invasive biopsies.
To find out more on the use of genomic testing to personalized radiation therapy I spoke with Javier Torres-Roca, M.D., associate professor of radiation oncology, Moffit Cancer Center, and co-founder of the genomics company Cvergenx. In this VIDEO he explained how genomics can be used to assess a patient's radiosensitivity, which can be used to increase or decrease the radiation that needs to be delivered to treat the tumor and spare surrounding healthy tissue.
To find out more about the use of liquid biopsies I spoke with Aadel Chaudhuri, M.D., assistant professor of radiation oncology, Washington University, St. Louis, Mo. In this VIDEO interview he explains his research on using blood tests to assess tumor response to radiotherapy.
An interesting technology that was discussed in sessions is the use of nanoparticle injection into the tumor to enhance the tissue's radio-sensitivity. I spoke with Nanobiotix, a company that developed a crystalline nanoparticle that enhances the effectiveness of RT several times-fold. The metallic-based particles also show up on CT scans so it can be used as a permanent fiduciary marker to track tumor response.
MRI-guided Radiation Therapy
The ViewRay MRIdian is currently the only FDA-cleared magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-guided radiation therapy system on the U.S. market, but there were two more companies with systems pending FDA review at ASTRO 2018. MRI offers excellent soft tissue detail and allows direct visualization of tumors, including real-time tracking of tumor movement to ensure the beam stays on target. Tissue response can also be viewed with the onboard MRI.
The Elekta Unity system will likely become the second FDA-cleared system. It is currently pending FDA 510(k) approval. It was the centerpiece of the Elekta booth at ASTRO. It gained European CE mark earlier this year and is being reviewed by the FDA. It uses a Philips 1.5T MRI system, which is a standard magnet strength in general radiology MRI systems. It should offer higher image quality than the ViewRay system, which uses a 0.3T imaging system.
The MagnetTx Aurora MRI-guided radiation therapy system was also shown at ASTRO 2018. This start-up company submitted for FDA 510(k) review this fall. The company has been developing the system over the past decade. It uses a unique cryogen-free 0.5T MRI system, so there is no need for a vent stack. It also offers a large 110 cm bore, allowing room for the patient table to be moved to align the iso-center of tumors with the linac beam.
Read more about MR-RT systems in the article "Market for MRI-based RT Could Soon Widen."
ITN visited one of the MRIdian install sites at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit. Watch the VIDEO of that visit and interview with Benjamin Movsas, M.D.
A Novel PET-guided Radiation Therapy System
Displayed for thw first time at ASTRO was RefleXion Medical's biology-guided radiotherapy (BgRT). It uses a novel positron-emission tomography, computed tomography (PET-CT) system combined with a linac in a single gantry that offers a new approach to real-time adaptive therapy.
It is the first system to utilize the cancer itself to guide radiation delivery, even in tumors that are moving. The system uses positron emission tomography (PET) to track the radioactive tracer uptake in cancer cells to lock onto the tumors and eliminate or reduce the need for margins to account for motion. The PET system triangulates the location of the radio tracer for accurate, 3-D, real-time tumor tracking. The RefleXion system also has the ability track and treat several sites at the same time.
The system does not yet have any regulatory approvals, but there are several luminary centers already interested in possibly acquiring this technology for use in clinical trials. Emory is one of the centers interested and I shot a VIDEO interview with Kristin Higgins, M.D., medical director of radiation oncology at the Emory Clinic at the Winship Cancer Institute, and associate professor, Department of Radiation Oncology, Emory University School of Medicine, on the technology.
Trends in Proton Therapy Systems
The key messages at ASTRO regarding proton therapy systems were that these are getting smaller, pencil beam therapy will likely become the standard of care in the coming years, and two new treatment methods may significantly cut treatment times and improve outcomes.
Varian and IBA showed new concepts with their systems to speed treatment delivery. Varian announced at ASTRO it is working on a way to deliver a single fraction, one second, very-high dose of protons to a tumor to enable a one day, one-and-done session called Flash therapy. The vendor said its newer cyclotron has the capability of delivering much higher proton dose rates than previous generation systems, enabling it to deliver ultra-high dose rates of 40-120 Gy per second.
IBA announced at ASTRO that the first patients have been treated using a Spot Scanning Proton Arc (SPArc) plan at the Beaumont Health Proton Therapy Center in Royal Oak, Mich. Instead of using a traditional series of beams that intersect a tumor and require the gantry or patient to be rotated for each beam, proton arc therapy leaves the beam on as it rotates around the patient, enabling much shorter therapy delivery times. Watch a VIDEO interview with Peyman Kabolizadeh, M.D., the medical director of Beaumont Proton Therapy Center, who talks about the use of proton arc therapy.
Read more in the article "Trends in Proton Therapy — Faster Therapy Delivery, Single-room Installs."
Tumor Tracking Imaging Using PET-CT
GE Healthcare showed an interesting new imaging technology that allows 4-D visualization of tumor movement during respiration on PET-CT called MotionFree. The technology now available on GE’s PET-CT scanners reduces blur caused by respiratory motion to make nuclear images much clearer. This can aid in identification of smaller tumors that otherwise would have been missed with conventional PET imaging. The MotionFree software also automatically detects and eliminates motion blur on PET scans and to enhance 4-D visualization. The correction algorithm improves overall PET image clarity, making the scans look more like CT images.
Find additional ASTRO coverage with links to late-breakers, videos and other news in "Late-breaking Radiation Therapy Clinical Trials at ASTRO 2018."
Learn more about recent trends in radiation oncology and treatment planning in the blog "The Hottest Topics in Medical Physics at AAPM 2018."
Related ASTRO 2018 Coverage:
Market for MRI-based RT Could Soon Widen
VIDEO "Editor's Choice of the Most Innovative Radiation Oncology Tech at ASTRO 2018
Smart Machines To Empower Oncology Docs and Patients, Say ASTRO Experts
Trends in Proton Therapy — Faster Therapy Delivery, Single-room Installs
Novocure Leverages Electricity Against Toughest Cancers
SBRT As Safe And Effective As Conventional RT For Some Prostate Cancer Patients


 April 18, 2024
April 18, 2024