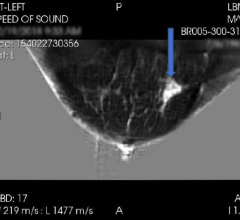
December 29, 2015 - The use of ultrasound (US) in detecting breast cancer has been shown to be comparable in its sensitivity to that of mammography and should be considered when testing for the disease according to a study published Dec. 28 in the JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
The number of breast cancers is increasing across the globe, with over 1.6 million new cases of the disease in 2010, resulting in the deaths of over 425,000 women. Additionally, 2.1 million new breast cancer cases are expected by 2030. While mammography is an effective method in detecting breast cancer in developed countries, it is not commonly available in less developed nations, and alternative methods, such as ultrasound, need to be tested.
To determine the effectiveness of using ultrasound to detect breast cancer, Wendie A. Berg, M.D., Ph.D., Department of Radiology, Magee-Womens Hospital, Pittsburgh, Pa., and colleagues recruited 2,809 women across 20 different sites in the United States, Canada, and Argentina to the American College of Radiology Imaging Network protocol 6666 breast cancer screening study. Of the participants, 2,662 completed three annual breast screenings by US and film-screen or digital mammography, and then had a biopsy or a 12-month follow-up.
The researchers found that the number of US screens to detect breast cancer was comparable to that of mammography, and found that there was a greater proportion of invasive and node-negative cancers in those who had US; however, there was also a greater number of false-positives among the women screened with US. While the false-positive rate of US exceeds that of mammography, the number of women recalled for extra testing becomes more comparable on incidence screening rounds, the authors write.
“Where mammography is available, US should be seen as a supplemental test for women with dense breasts who do not meet high-risk criteria for screening MRI and for high-risk women with dense breasts who are unable to tolerate MRI,” Berg said.
For more information: www.oxfordjournals.org/our_journals/jnci/press_releases/bergdjv367.pdf


 April 18, 2024
April 18, 2024