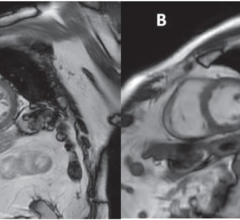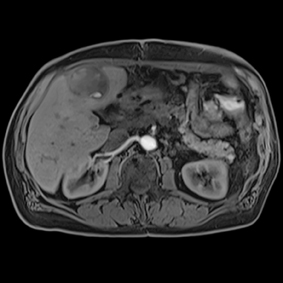
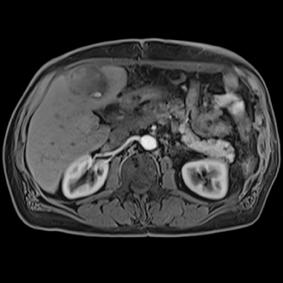
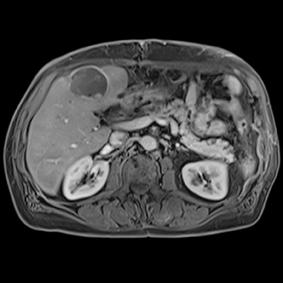
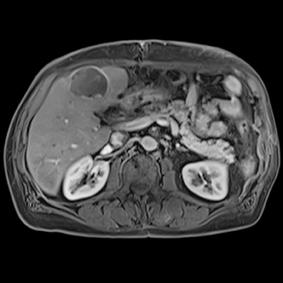
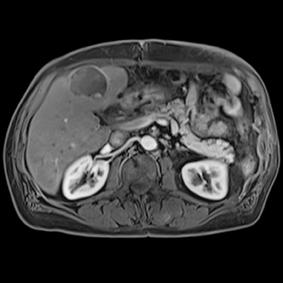
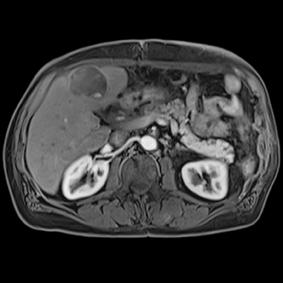
This series of images taken with TwistVibe show how the new technology enables radiologists to catch the correct time point of lesion enhancement within the arterial phase. With TWIST-VIBE, it is now possible to generate multiple stacks of images from the arterial phase to follow the lesion enhancement over time. With that, other so-far-unseen lesions may become visible. Images courtesy of University Hospital IKRN, Mannheim, Germany.
The use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is growing both domestically and internationally, rebounding from the slump that hit the market in 2008-2009. Vendors have seen an increase in system utilization. According to Stuart Clarkson, senior director of the MR business unit at Siemens Healthcare, “We’ve seen approximately 3 to 4 percent growth in the number of scans this year versus the previous year. So, we like to think that MR is still a growing imaging modality.”
This growth can be attributed to a number of factors including an aging population and increased awareness of new MR capabilities. Using MRI, physicians are able to measure early response to treatment and provide early diagnosis, and address decisions that have not been commonly addressed in the past.
As the use of MRI grows, physicians can expect to see an increase in the type of scans done with MR. This phenomenon is also being driven by decreasing budgets. As radiology budgets get smaller, many providers are looking for equipment that gives them the most variety of use for the price. “A lot of the providers that we talk with are trying to get the most out of their scanners — they’re definitely using it in more areas. I think that’s why you will see that cardiac is mentioned a little bit more, as well as oncology. We’re also starting to see MR being used in radiation therapy,” said Brady Heiner, author of the KLAS report, “MRI 2013: Sorting Through the Noise.”
Better Patient Experience
Many current advances in MRI technology and applications are geared toward making the patient experience less daunting. Manufacturers are focusing on the two most disturbing aspects of MRI exams: the narrowness of the bore and the exam noise level. While wide-bore technology has helped ease the anxiety of larger and claustrophobic patients, a current trend impacting this technology is to cut back on the volume of noise that is emitted. “Everyone wants to get quieter. I think that’s definitely the direction of the future,” said Heiner.
GE released its Silent Scan noise reduction technology at the 2012 Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) annual meeting, and according to the KLAS report, “Silent MR is resonating with GE and non-GE users.” At RSNA 2013, Siemens launched its Quiet Suite, which significantly reduces noise for brain and orthopedic scans. Toshiba has its Pianissimo technology, which reduces acoustic noise on average by about 90 percent, for 15 years. “Pianissimo is a complete system-based solution, not sequence-based. Our scanner is quiet for all exams and for all types of patients. It’s not something that you can turn on or off. It is always quiet and is available as a standard on all Toshiba 1.5 and 3.0 Tesla platforms,” said Suresh Narayan, senior manager, market development, Toshiba MR business unit.
According to the KLAS report, however, many of the silent technologies are limited because they are only available for certain scans. “You’re only able to use silent technologies for certain scans at this point, but that is being expanded and growing as far as the different scan types that you can do,” stated Heiner.
Ioannis Panagiotelis, Ph.D., chief marketing officer, GE Healthcare MR, said that initially, Silent Scan was only available for a few types of neuro scans. “Now, as of RSNA 2013, we have expanded to more sequences and more contrasts. We’re working on expanding it to other body parts to the complete portfolio,” he said.
Siemens is also working on expanding its Quiet Suite technology. “There are some sequences that are still quite difficult to make quiet, but we’ve got a broad range of sequences that can make use of the technology,” said Clarkson.
Streamlining Products, Workflow Efficiency
Manufacturers are continuously working toward improving efficiency. In response to customer needs, manufacturers have released applications to make MR run more quickly, make it more comprehensive and increase efficiency and patient throughput. “There are some really stringent needs that are being put on manufacturers to make our equipment more streamlined and to be more productive from a workflow and throughout standpoint. This trend will continue well into the future,” said Narayan.
One way to increase efficiency is by making the technology faster. “MR seems to have this continual drive to go faster and faster. We’ve seen significant improvements in technology with reductions in scan times in all areas,” said Clarkson. According to Panagiotelis, application speed is also increasing. “People would like to see more and more applications that are faster to execute and faster to run, and at the same time easier to read — easier to derive a clinical conclusion.”
Manufacturers have also addressed efficiency issues by making applications more intuitive for the user. According to feedback in the KLAS report, Toshiba providers “want the Titan to be easier to use,” and stated that the M-Power user interface “requires too many clicks and too much tech interaction.” Beverly Plost, director, Toshiba MR business unit, noted some of Toshiba’s newest interface enhancements. “Our M-Power upgrades are designed for the simplified user interface with a lot of automation built in. It adds a whole new dimension of automated tools that improve not only the technologist’s experience but also the patient experience.”
Pushing the Limits of MR
As MRI popularity increases, manufacturers are exploring novel ways to use the equipment in areas such as abdominal imaging, which has generally been dominated by computed tomography (CT). “We believe that MR is actually a better tool for detecting small lesions because of its improved contrast-to-noise ratio. We’ve been spending a lot of time making abdominal images easy and faster for patients and technologists,” said Clarkson. “There are some new sequences that Siemens showed at RSNA that allow patients to free breathe, and we can still get exquisite details of particularly the liver, which is a major organ for oncology imaging,” he explained. The Freezeit application, which received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval in November 2013, is available with the StarVibe and TwistVibe sequences. The StarVibe sequence is designed to enable free-breathing, contrast-enhanced liver imaging, and the TwistVibe sequence is designed to enable correct contrast imaging in dynamic liver MRI for all patients and lesions. Freezeit is currently available on the Aera wide-bore 1.5 Tesla and Skyra wide-bore 3.0 Tesla systems.
GE is also pushing the limits of MRI. In late 2013, the company released its Mavric SL application, which enables physicians to perform MRI scans on patients that have metal implants. “While in the past these patients were not able to be scanned diagnostically with MRI or other types of imaging, this particular sequence significantly reduces the artifact effect that causes image distortion,” said Panagiotelis. GE pioneered the application at RSNA 2012. The company is also working on an integrated positron emission tomography (PET)/MR technology that gives physicians the ability to perform simultaneous examinations with no time or image quality compromise. The technology was presented at RSNA 2013, and GE expects to release it to the market in the near future.
Toshiba has already developed several new applications to make MR more clinically comprehensive. “The systems marketed and sold today are clinically comprehensive,” said Narayan. With its focus on non-contrast imaging, Toshiba is also making the machines more inclusive. “If you look at the disease profile of the United States, and even globally, you are seeing increasing trends in diabetes and obesity. Several of those patients cannot take a gadolinium- or contrast-enhanced exam,” Narayan explained. “That is where we have a suite of applications or techniques where we can image vasculature pretty much anywhere in the body without injecting contrast.” Toshiba has also introduced its Pediatric Suite — a new coil for pediatric imaging that has a customized design specifically for imaging the head, neck, spine and body for infants from a few pounds to older children up to 50 pounds.
Leading With Innovation
Although the U.S. market is very advanced and is by far the innovation engine, U.S. manufacturers will have to continue this momentum because according to Panagiotelis, international markets are rapidly adopting MR. As MR expands to different areas of medicine and the advantages of the technology continue to be realized, manufacturers and physicians can expect the market to grow around the world. “When more manufacturers from emerging countries appear, the market is going to get more commoditized, then we will really need to be able to differentiate. Innovations are the strategies that will help us to protect our position in the market,” he concluded.


 April 17, 2024
April 17, 2024