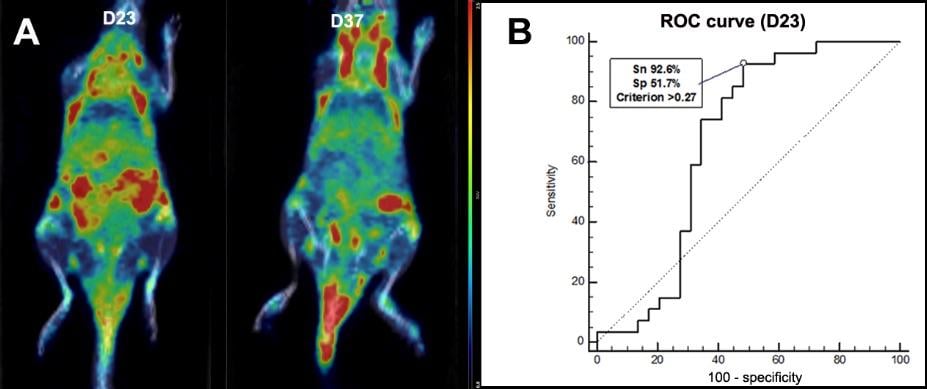
Coronal 18F-FEDAC PET/CT section of a mouse with collagen-induced arthritis. (A) On day 23 and day 37, increased uptake is noted in the front and hind paws of this mouse with collagen-induced arthritis. (B) Predictive performance of day 23 18F-FEDAC uptake for the development of clinical arthritis. ROC = receiver operating characteristic; Sn = sensitivity; Sp = specificity. Credit: Seoul National University and Ewha Womans University, Seoul, South Korea
May 17, 2018 — A novel positron emission tomography (PET) tracer developed by Korean researchers can visualize joint inflammation and could provide early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis, a common autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of joints and can lead to deformity and dysfunction. The study is reported in the featured basic science article in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine’s May issue.
Activated macrophages, white blood cells that help protect the body from harmful bacteria and infected cells, are known to play a pivotal role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) development. Focusing on the translocator protein (TSPO), which is abundant in activated macrophages, researchers developed fluorine-18 (18F)-FEDAC, a radiolabeled ligand that targets TSPO and binds to it.
“This study is novel because it showed the value of 18F-FEDAC PET as an inflammation biomarker for early detection of rheumatoid arthritis, even before onset of clinical symptoms of joints,” explained Gi Jeong Cheon, M.D., Ph.D., of Seoul National University College of Medicine in Seoul, Korea.
For the study, 18F-FEDAC was tested in a mouse model, using both 18F-FEDAC and 18F-FDG PET imaging. Microscopic examinations of tissue were performed to evaluate macrophages and TSPO expression.
Results showed increased TSPO mRNA and protein expression in activated macrophages, and uptake of 18F-FEDAC in activated macrophages was higher than it was in non-activated cells. In addition, 18F-FEDAC uptake by arthritic joints increased early on (day 23), whereas 18F-FDG uptake did not. However, 18F-FDG uptake by arthritic joints increased at later stages (day 37) to a higher level than 18F-FEDAC uptake.
This early study demonstrates that 18F-FEDAC makes it possible to see active inflammation sites in arthritic joints by targeting TSPO expression in activated macrophages, and it suggests imaging with 18F-FEDAC could be useful when RA is suspected.
Cheon pointed out, “Early treatment can reduce the progression of joint destruction and enhance the effect of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs or target drugs, because the burden of inflammatory reaction is smaller in the very early phase of RA.” He noted, “We observed that 18F-FEDAC uptake increased in paws of murine RA models in association with TSPO expression of activated macrophages, even before the onset of clinical symptoms of arthritis. 18F-FEDAC can help us to find which patients will actually progress to clinically significant rheumatoid arthritis and need treatment.”
Reflecting on the comparison of 18F-FEDAC PET with 18F-FDG, Cheon stated, “From our data, we found that each tracer may be useful for different information about arthritis — 18F-FEDAC for early detection of subclinical arthritis and 18F-FDG for measuring disease activity of symptomatic arthritis. These findings are expected to contribute to the improvement of personalized therapeutic outcomes by expanding the scope of molecular imaging and nuclear medicine.”
For more information: www.jnm.snmjournals.org


 May 30, 2025
May 30, 2025