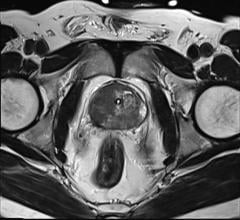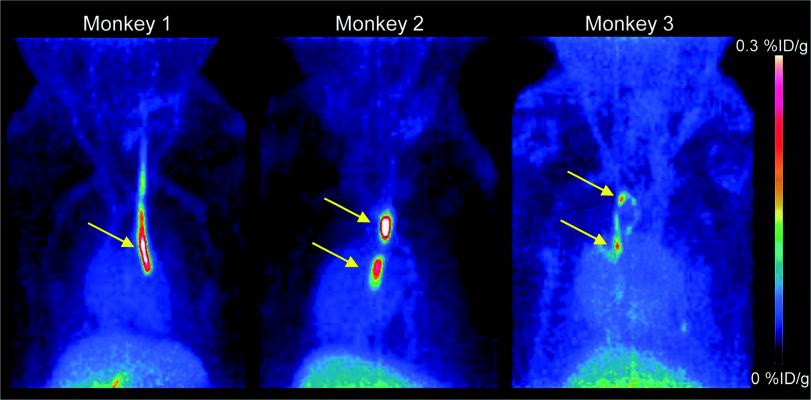
PET images (MIP 0-60 min) of three Cynomolgus monkeys. Strong signals are detected at the sites where inserted catheters had roughened surfaces. Almost no other background signal is visible. Only accumulation in the gallbladder becomes visible at the bottom of the image. Credit: Piramal Imaging GmbH, Berlin Germany.
July 7, 2017 — Blood clots in veins and arteries can lead to heart attack, stroke and pulmonary embolism, which are major causes of mortality. In the featured article of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine’s (JNM) July 2017 issue, German researchers show that targeting GPIIb/IIIa receptors, the key receptor involved in platelet clumping, with a fluorine-18 (18F) labeled ligand is a promising approach for diagnostic imaging. Current imaging modalities rely on structural characteristics, such as vascular flow impairment, and do not address the critical molecular components.
“Currently available diagnostic techniques of thrombus [blood clot] imaging rely on different modalities depending on the vascular territory,” explained Andrew W. Stephens, M.D., Ph.D., of Piramal Imaging GmbH, Berlin, Germany. “A single imaging modality that could visualize thrombi from various sources in different anatomic regions would be very valuable.”
For this preclinical study, researchers successfully developed the novel small molecule tracer 18F-GP1 for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging that binds with high affinity to GPIIb/IIIa receptors. 18F-GP1 showed a strong accumulation at the site of thrombus formation, and its binding ability was not affected by anticoagulants such as aspirin and heparin. The tracer showed rapid blood clearance, and PET imaging in a Cynomolgus monkey model demonstrated the detection of small venous and arterial clots, endothelial damage and emboli in the brain.
Due to the favorable pre-clinical results, a first-in-human study of 18F-GP1 is currently underway. Early results from an interim analysis confirm the preclinical data and were presented at the 2017 Annual Meeting of the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI), June 10-14 in Denver.
“Although the current studies are preliminary, 18F-GP1 may provide not only more accurate anatomic localization, but also information of the risk of the clot growth or embolization,” Stephens pointed out. “This may lead to changes in clinical intervention to the individual patient.” Addressing the use of anticoagulants to treat blood clots, he noted, “These drugs can cause significant and life-threatening bleeding. There is a critical need to balance the risk of bleeding against the risk of clotting in each patient. 18F-GP1 may in the future assist in this important decision.”
For more information: www.jnm.snmjournals.org

 April 22, 2024
April 22, 2024