October 18, 2016 — The association between provider case volume and outcomes has long been suggested in cancer care. A Yale Cancer Center team has completed a review of outcomes for patients with locally advanced squamous cell head and neck cancers treated with intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and found a distinct association between higher-volume treatment centers and improved overall survival. The findings were presented Sept. 26 at the American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ASTRO) meeting in Boston.
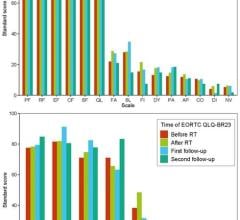
This study used the National Cancer Data Base to analyze 9,817 patients and found that patients treated at higher-volume facilities were more likely to have shorter radiation therapy duration than those at lower volume facilities.
The research team’s findings also revealed there was a 5.7 percent decreased hazard of death per additional 20 patients treated per year per facility. When annual facility case volume was defined based on a threshold of 95 cases/year (90th percentile), there was a 17.5 percent decreased hazard of death for higher-volume versus lower-volume facilities.
“Our findings suggest a strong relationship between higher-volume radiation therapy facilities and improved overall survival for patients treated with IMRT for locally advanced head and neck cancers,” said Henry S. Park, MD, MPH, first author on the study and a chief resident in the Department of Therapeutic Radiology at Yale School of Medicine. “Further investigation should focus on the role of other factors potentially underlying this association, including radiation contouring, education, multidisciplinary communication, and toxicity management.”
For more information: www.astro.org


 March 28, 2024
March 28, 2024