December 10, 2009 - Better dose conformality can be reached with intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) in comparison to three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy techniques - as used in dose escalation studies - offering an additional opportunity for healthy tissue protection, reports Michael Pinkawa, M.D., in an abstract of his study published in UroToday.com.
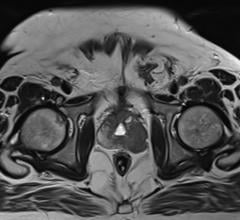
The study's objective is to compare the dose distribution in IMRT treatment plans with and without a simultaneous integrated boost (IB) after performing a PET/CT with 18F-choline for treatment planning. Dose-volume histograms and equivalent uniform doses (EUD) were evaluated and normal tissue complication probability (NTCP) for the bladder and rectum compared.
Dr. Pinkawa found that while improved biochemical control rates for prostate cancer have been consistently shown in randomized three-dimensional (3D) conformal radiotherapy dose escalation studies, this benefit was associated with the problem of increased rectal toxicity. The increasing implementation of image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) allows a reduction of safety margins around the clinical target volume (CTV). Thus, the same or improved local tumor control with lower rectal toxicity due to reduced rectal volume within the target volume can be expected.
Dr. Pinkawa also points to dose-painting as another advantage associated with IMRT as areas with a higher risk of tumor recurrence or a higher tumor load can be covered with larger doses in the same fraction. In view of an often multifocal micrsoscopic spread of prostate cancer - not possible to delineate with the presently available imaging modalities - the whole prostate must still be covered by an effective dose.
He found that treatment planning with a simultaneous integrated boost allows an individually adapted dose escalation. The boost volume, as defined by a tumor-to-background uptake ratio >2 in a PET/CT with choline, correlated with several well-established prognostic parameters. His founding indicated that the therapeutic ratio can be improved by a considerable dose escalation to the macroscopic tumor site without considerably increasing the NTCP for the rectum and bladder.
For more information: www.urotoday.com


 March 28, 2024
March 28, 2024