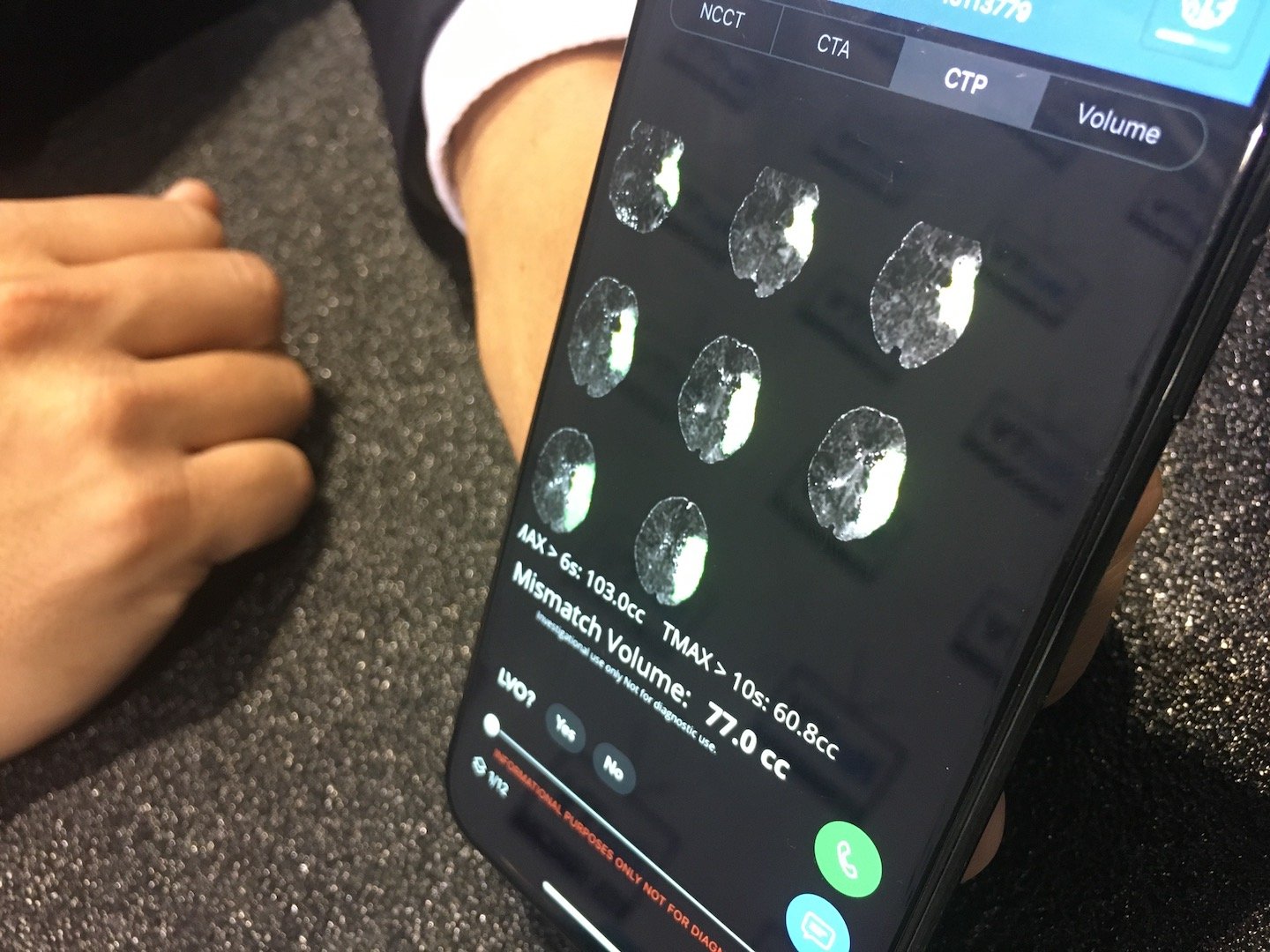
Brain images that have been pre-reviewed by the Viz.AI artificial intelligence software to identify a stroke. The software automatically sends and alert to the attending physician's smartphone with links to the imaging for a final human assessment to help speed the time to diagnosis and treatment. Depending on the type of stroke, quick action is needed to either activate the neuro-interventional lab or to administer tPA. Photo by Dave Fornell.
With its increasing role in medical imaging, artificial intelligence (AI) gradually is becoming a go-to technology for building custom healthcare software to diagnose a wide range of diseases, from diabetic retinopathy to skin cancer. With several vendors now working on stroke detection AI algorithms and a few of these recently gaining U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval, stroke may be the next frontier to conquer.
According to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), stroke puts a significant burden on the U.S. healthcare, being one of the leading causes of long-term disability and accounting for $34 billion in yearly costs for care delivery, medications, and missed work days. Indeed, a major part of the expenditures related to stroke arises from a lengthy rehabilitation period. For most acute conditions, discharge from the hospital means that the patient has almost or completely recovered. But when it comes to stroke, discharge is just the beginning of a journey towards recovery.
What Healthcare can do for Stroke Patients
Best case would be to prevent patients from having a stroke, or, at least, accelerate time-to-diagnosis and thus minimize the brain damage. If a stroke is diagnosed immediately, the patient may fully regain their mobility, self-care and social skills, progress sooner, or experience only a slight decline
But an inaccurate diagnosis may lead to dire consequences. Ischemic stroke is the most common type of this condition, and it is usually treated with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) to dissolve the blood clots and restore the blood flow to the brain. However, this medication can be deadly to a patient with a hemorrhagic stroke, because it will increase the internal bleeding. In turn, a hemorrhagic stroke may require surgical intervention or coil insertion to stop the bleeding. Deciding on the stroke type can be challenging, but health specialists still need to figure it out quickly to save the patient’s life and functionality.
The current maturity level of artificial intelligence technology can unlock numerous opportunities for stroke care, from uncovering the underlying risks to develop stroke in certain patient groups to alerting health specialists about suspicious abnormalities on medical scans during triage.
Preventing Stroke and Rewinding Risks
CDC also notes that stroke is preventable in up to 80 percent of cases if the patients recognize and mitigate the risks in due time. However, most health risks are related to a patient’s habits and choices in nutrition, physical activity, and lifestyle. Therefore, a patient might tend to disregard their physician’s suggestions.
A study from Google’s AI team attempts to throw abstractions away and show the patients their future by analyzing retinal images, extracting their personal health risks, and making predictions based on the knowledge received. Their system can extract a range of risk factors critical for the occurrence of cardiovascular disease and stroke, such as body mass index (BMI), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), systolic and diastolic blood pressure, as well as smoking status. The researchers reported their algorithms succeeded in predicting the chances of particular patients developing stroke or heart attack in a five-year period with a 70 percent accuracy.
Another recent U.K. research study concentrated on analyzing CT and MRI scans to detect and grade the small vessel disease (SVD). This is a neurological condition that hinders the blood supply of the brain, causing stroke and dementia.
While it can be diagnosed via CT and MRI scans without the bias or risk to confuse it with a mimicking condition, the precise SVD’s severity evaluation is rather complex. In the meantime, health specialists need to grade the disorder as accurate as possible. For example, if a patient has an ischemic stroke while having severe SVD, the administration of tPA can lead to a brain hemorrhage, increasing the damage to patient health. The researchers claim that their algorithm was able to achieve an 85 percent accuracy in estimating the SVD severity from CT and MRI scans, offering health specialists an explicit knowledge about the patient’s health risks related to different treatment options. They hope that such systems will be applied both to making balanced decisions for acute stroke and to enabling precise dementia diagnosis and monitoring.
Early Diagnosis With FDA approval
AI’s superpower also helps define the stroke type shortly after the onset, detecting the slightest deviations on the CT and MRI scans. Machine learning algorithms can distinguish an ischemic stroke from a hemorrhagic or other types and also reduce the possibility to overlook other conditions, such as meningitis, seizure, encephalitis, acute demyelination, abscess and subdural hematoma.
In early 2018, FDA approved an AI algorithm for use in a clinical decision support system for triage. Called Viz.AI Contact, it can analyze CT scans and detect stroke signs in medical images, making a preliminary diagnosis. If the system suspects a stroke in a particular patient, it notifies a neurovascular specialist about the findings via a smartphone or a tablet. The specialist’s attention will be refocused to the most acute cases, while the radiologist can proceed with reviewing less urgent scans. This AI-enabled process optimization can ensure timely care for patients who may not be able to pull through the standard review procedure without risking their health or even life.
AI-enabled Stroke Battle Begins Now
Surviving a stroke is only a starting point of the patient’s fight for their full and independent life. The sooner a person receives adequate medical care, the more they can achieve during the rehabilitation, hopefully up to regaining their mobility and social skills completely. Artificial intelligence can support health specialists and provide them with actionable insights to accelerate diagnosis and ensure accurate medication and intervention decisions in the shortest possible time after the stroke onset. It can even help reduce the risk of developing the condition in some patients, eliciting subtle warning patterns and alerting the clinicians about the upcoming crisis.
Let us not forget about the FDA support. When the agency shows its dedication to technology, healthcare can not resist. With AI becoming the approved approach for clinical decision support and showing huge potential in helping many patients avoid or survive a stroke with minimal decline in communicative and motor functions, we expect the tidal wave of similar solutions emerging on the market and becoming the standard of preventive and reactive stroke care.
Editor’s note: Author Inga Shugalo is a healthcare industry analyst at Itransition, a custom software development company headquartered in Denver, Colorado. She focuses on Healthcare IT, highlighting the industry challenges and technology solutions that tackle them. Inga’s articles explore diagnostic potential of healthcare IoT, opportunities of precision medicine, robotics and VR in healthcare and more.


 April 24, 2024
April 24, 2024